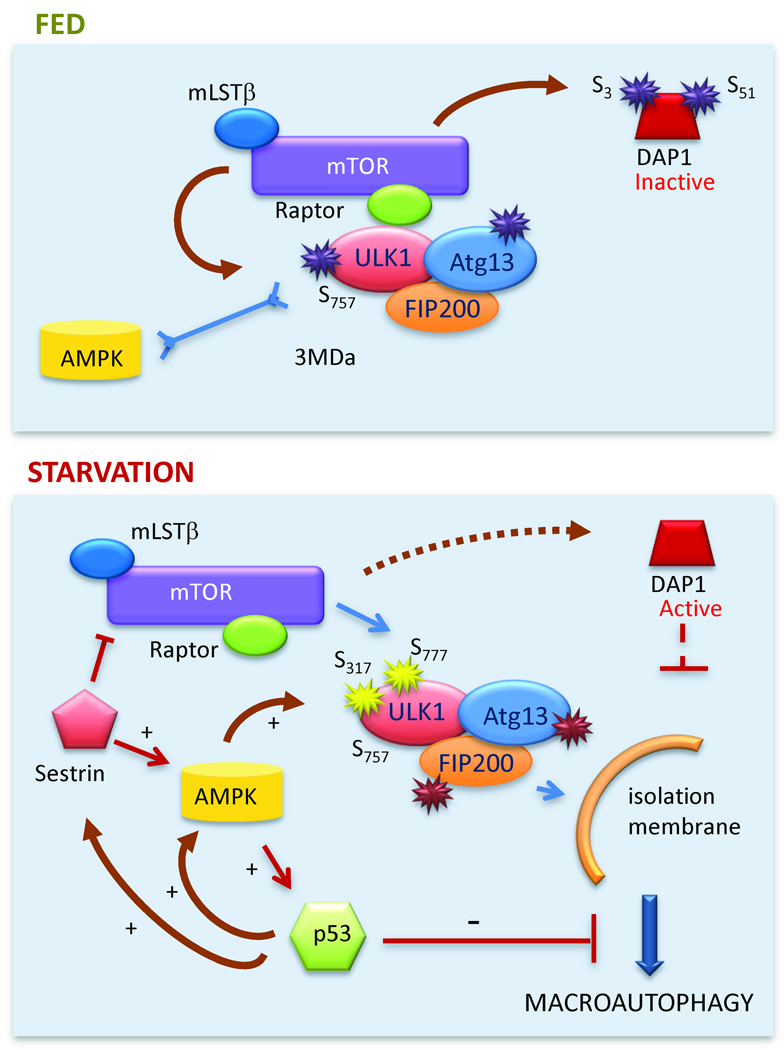
Figure 2. Nutritional regulation of macroautophagy.
Top: Under normal nutritional conditions mTOR 1) phosphorylates ULK1 which locks the ULK1-ATG13-FIP200 complex at the TORC1 complex and prevents its interaction with AMPK, and 2) inactivates DAP1 by phosphorylation. Bottom: During starvation, AMPK phosphorylates ULK1 favoring its release from TORC1 and its association to the site of isolation membrane formation. Reduced mTOR activity decreases DAP1 phosphorylation that through its inhibitory effect on macroautophagy prevents abnormal upregulation of this pathway. The positive feedback loops between AMPK, sestrins and p53 are shown. Independent of its transcriptional activity, cytosolic p53 can exert a direct inhibitory effect on macroautophagy.