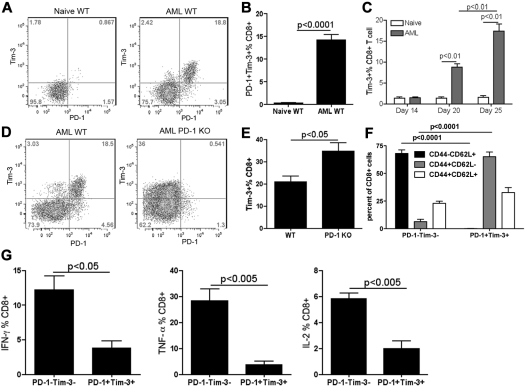
Figure 2.
AML-induced PD-1+Tim-3+ liver CD8+ T cells in WT mice were dysfunctional. (A-C) B6 WT mice were injected intravenously with 106 C1498FFDsR. Liver leukocytes were isolated 14, 20, and 25 days post-AML injection. PD-1 and Tim-3 expression was determined by FACS. PD-1 and Tim-3 coexpression detected on liver CD8+ T cells 25 days post-AML injection is shown in flow dot plot (A) and bar graph (B). (C) Time course of Tim-3 expression on liver CD8+ T cells as AML progression in mice is shown. Tim-3 was up-regulated at a late phase of disease (day 20 and 25 but not day 14). (D-F) WT and PD-1 KO mice (3-4 mice/group) were injected with 106 C1498FFDsR. Liver leukocytes were isolated 25 days post-AML injection. PD-1, Tim-3, CD44, CD62L, and intracellular cytokine production was determined by flow cytometry. (D-E) Tim-3 was expressed at a higher level in PD-1 KO mice compared with WT mice. (F) Majority of PD-1+Tim-3+ CD8+ T cells was CD44+CD62L−, while PD-1−Tim-3− CD8+ T cells were mainly CD44−CD62L+. (G) PD-1– and Tim-3–coexpressing CD8+ T cells from WT mice are highly deficient in producing IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2 compared with PD-1-Tim-3- fraction. Data were pooled from 2 individual experiments.