Figure 2.
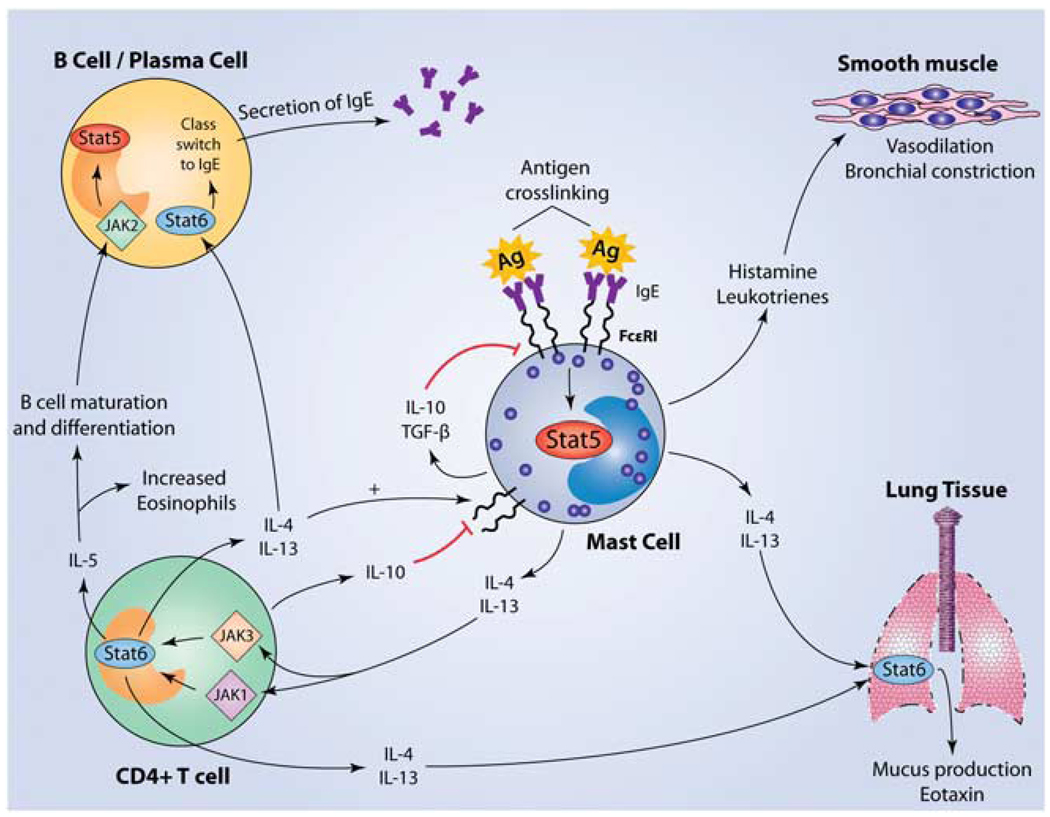
Activation of mast cells initiates a cascade of events resulting in Th2 polarization and both positive and negative feedback regulatory loops. Mast cells are activated when antigen binds to specific IgE molecules bound to FcεRI receptors on the surface of the mast cell. Subsequent crosslinking results in signaling through the IgE receptor and activation of multiple pathways, including the JAK–STAT pathway. STAT5 has been shown to be required for IgE-mediated cytokine production as well as histamine and leukotriene release.82 Although histamine and leukotrienes cause the early-phase response through vasodilation and bronchial constriction, cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13 mediate the late-phase response. IL-4 and IL-13 share the ability to signal through the IL-4Rα, which is associated with JAKs 1 and 3, leading to the activation of STAT6. STAT6 activation leads to polarization toward a T helper 2 phenotype, resulting in the release of cytokines such as IL-10, IL-6, IL-5, IL-9, IL-4 and IL-13. IL-4 and IL-13 can both signal through STAT6 in B cells, inducing isotype switching and subsequent production of IgE, which can bind FcεRI on mast cells.113–115 Unlike the allergy-promoting effects of IL-4 on B cells, IL-10 has an inhibitory effect on mast cells, leading to the suppression of both c-kit and FcεRI expression, accompanied by the induction of apoptosis.116–122 Mast cell-derived transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) also acts as a negative regulator, working in an autocrine manner on mast cells.123–126 IL-5, on the other hand, supports the differentiation, survival and proliferation of both B cells and eosinophils, partly mediated through JAK2–STAT5 signaling, in conjunction with other pathways.127,128 Further recruitment of eosinophils occurs through production of the chemokine eotaxin, largely by cells of the airway epithelia. Eotaxin can be induced by the cytokines IL-4, IL-13 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), which are derived from Th2 cells and possibly directly from mast cells themselves.129–132