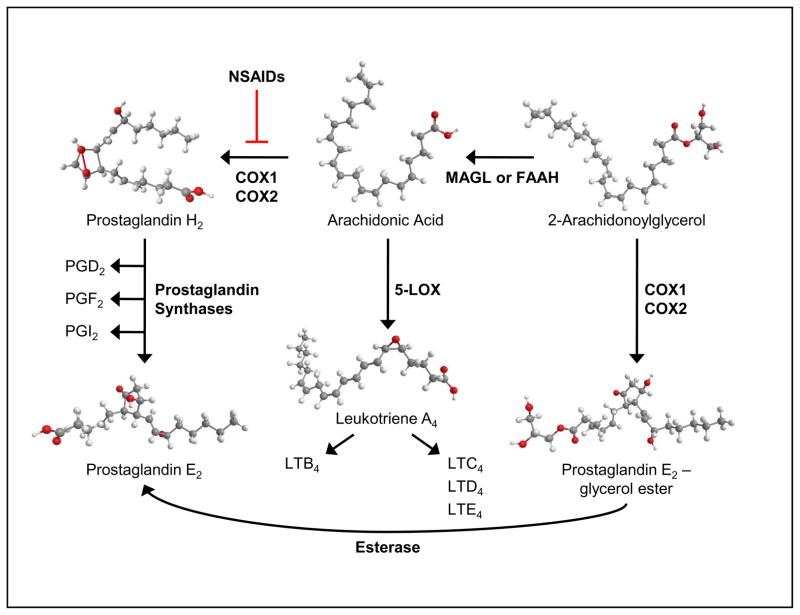
Figure 1. Schematic of eicosanoid biosynthesis.
Activation of c-phospholipase A2 releases arachidonic acid from phospholipids. Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which can be inhibited by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), convert arachidonic acid into the Prostaglandin H2 intermediate, which is then converted to the various prostaglandins by distinct prostaglandin synthases . Similarly, 5- lipoxygenase (5-LOX) converts arachidonic acid into Leukotriene A4 (LTA4) and then synthesis proceeds to the various leukotrienes. Endocannabinoid (2-Arachidonoylglycercol) is catabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) or monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) and can be converted into alternate prostaglandin forms.