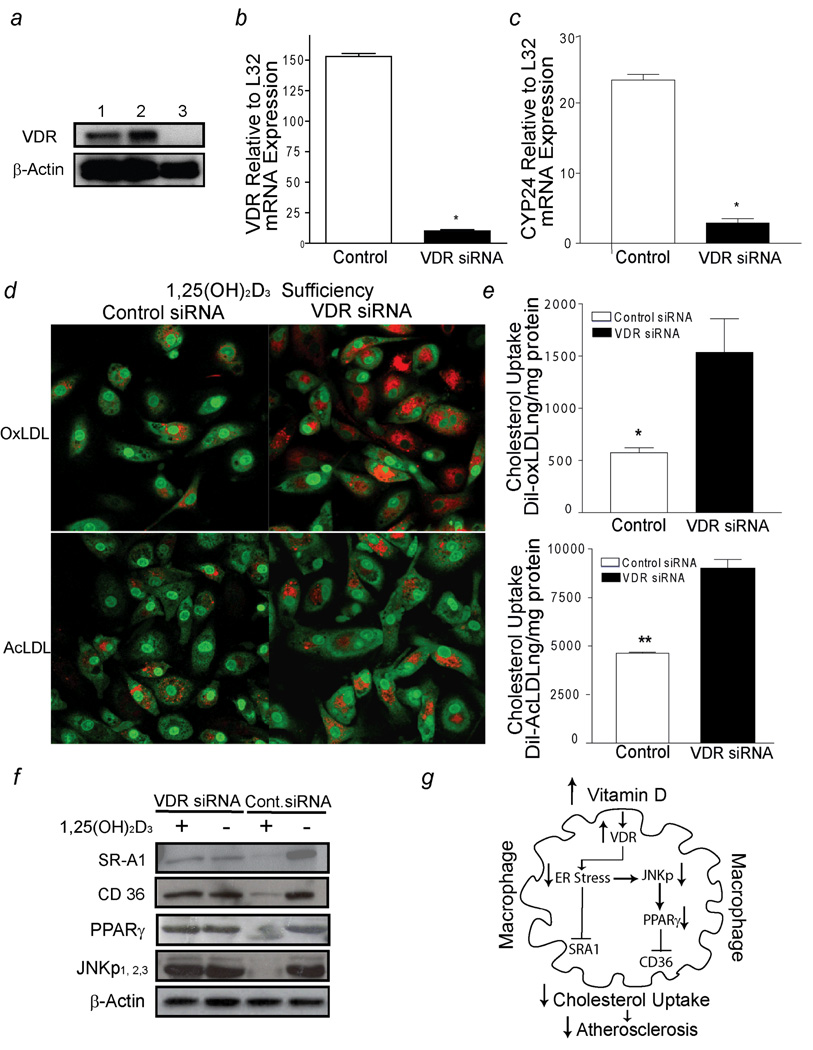
Figure 6.
1,25(OH)2D3 activation of VDR signaling prevents macrophage cholesterol uptake in diabetics (group A). a, VDR receptor expression (top-panel) and β-actin (bottom-panel). Lines 1–2, siRNA-control infected cells; line 3, VDR-siRNA infected cells. b and c, qPCR of VDR mRNA and CYP24 mRNA expression in response to 1,25(OH)2D3 supplementation in macrophages infected with either VDR-siRNA (black-bars) or control-siRNA (white-bars) lentivirus, respectively (n=8 per group). (* p< 0.0001 vs. control-siRNA macrophages). d, Cholesterol uptake assessed by confocal microscopy. Red represents labeled cholesterol uptake after Dil-oxLDL (top-panel) or Dil-AcLDL (bottom-panel) stimulation; green fluorescence represents nuclear counterstains. e, Cholesterol uptake after incubation with Dil-oxLDL (top-panel) or Dil-AcLDL (bottom-panel) in macrophages cultured in 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented media after infection with siRNA lentivirus (n=5). (*p <0.01; *p <0.02 vs. VDR-siRNA macrophages). f, SR-A1, CD36, PPARγ, JNKp expression from macrophages infected with either VDR-siRNA or control-siRNA lentivirus cultured in vitamin D-deficient media or 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented media. g, Mechanistic pathways involved in 1,25(OH)2D3 suppression of foam cell formation.