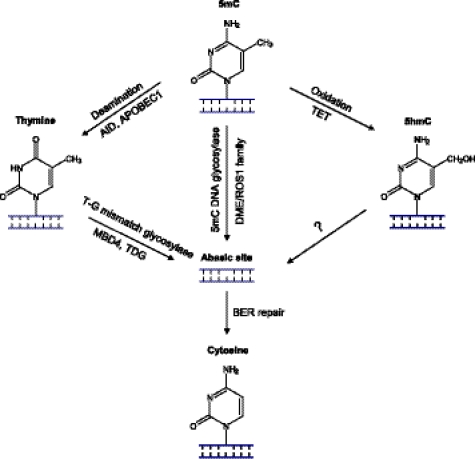
FIGURE 3.
Models for DNA demethylation mechanisms involving BER. In plants, the 5mC base can be directly removed by the DME/ROS1 family of 5mC DNA glycosylases, resulting in an abasic site that is repaired by the BER process. In mammals, no efficient 5mC glycosylases have been conclusively identified, and an alternative pathway initiated by deamination of 5mC has been proposed. Candidate deaminases include AID and APOBEC1, which convert 5mC to thymine. The resulting thymine could be repaired by BER initiated by a T-G mismatch glycosylase such as MBD4 or TDG. Recently, it has been shown that mouse and human TET family proteins can catalyze conversion of 5mC to 5hmC, a new modified base found in mammalian DNA. It is tempting to speculate that 5hmC could be repaired by a BER process, although, so far, no 5hmC DNA glycosylases have been identified.