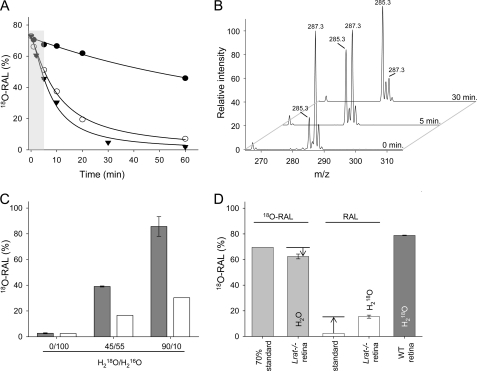
FIGURE 2.
Incorporation of 18O into at-RAL liberated from photoactivated Rho. A, exchange of 18O in synthetic at-[18O]RAL upon incubation in an aqueous solution containing 50% methanol (●), 1% BSA (○), or liposomes (▾). The 5-min time frame used for these experiments is indicated by the gray background. B, representative mass spectra indicate changes in the isotopic composition of at-[18O]RAL upon incubation in 10 mm Bistris propane buffer, pH 7.0, in 70% H218O with 100 mm NaCl and 1% BSA. The peak at m/z 285.3 corresponds to at-RAL ([M + H]+). The 2-Da shift in mass of at-[18O]RAL is indicated by the ion at m/z 287.3 ([M + H]+). C, incorporation of 18O into at-RAL released from photobleached Rho. Purified bovine ROS washed and resuspended in buffers containing various ratios of H218O were extracted with hexane, and the retinoid composition was examined by MS. The pool of analyzed at-RAL was significantly enriched in 18O. The ratio between at-RAL and at-[18O]RAL closely reflects the water composition present in the experimental samples (gray bars). The theoretical percentage of at-[18O]RAL that could be produced from unlabeled at-RAL due to oxygen back-exchange into buffers present in the samples is shown (white bars). D, retinal composition and oxygen back-exchange in isolated mouse retina. at-RAL or at-[18O]RAL (300 pmol) was added to homogenized retinas isolated from Lrat−/− mice and washed with buffers containing H218O or H2O. Samples were incubated on ice for 5 min and extracted with hexane. Oxygen back-exchange did not exceed 15% in the examined samples (light gray and white bars). WT mouse retinas washed with 90% H218O-containing buffer and exposed to light under similar experimental conditions revealed the presence of at-RAL highly enriched in 18O (dark gray bar). All data represent averaged values of three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate.