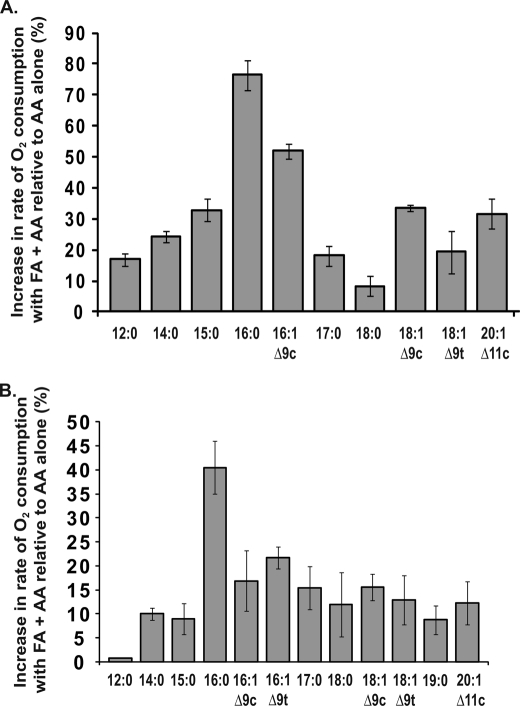
FIGURE 3.
Effects of saturated and monounsaturated FAs on AA oxygenation by huPGHS-2. Results are shown as a percentage of the rate of increase for O2 electrode assays of COX activities of huPGHS-2 with FAs (25 μm) in combination with AA (5 μm) versus 5 μm AA alone (A) and FAs (5 μm) in combination with AA (2 μm) versus 2 μm AA alone (B). Rates were determined by measuring O2 consumption using an O2 electrode as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The results in A and B are each from a single experiment involving triplicate determinations. The error bars indicate ± S.D. FA designations and common names are as follows: 12:0, lauric acid; 14:0, myristic acid; 15:0, pentadecanoic acid; 16:0, palmitic acid; 16:1 Δ9c, palmitoleic acid; 16:1 Δ9c, palmitelaidic acid; 17:0, heptadecanoic acid; 18:0, stearic acid; 18:1 Δ9c, oleic acid; 18:1 Δ9t, elaidic acid; 20:1 Δ11c; Δ11-eicosaenoic acid.