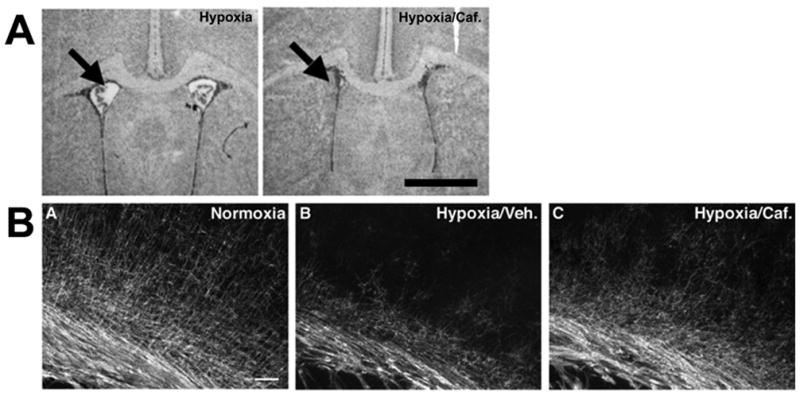
Figure 7. Cardiac A1ARs protect against hypoxia.
Embryos exposed to hypoxia for 2 days in utero from E8.5-10.5 were not growth retarded compared to room air controls, but embryos exposed to hypoxia in utero from E10-12.5 exhibited significant growth retardation. Embryos exposed to hypoxia for 3 days demonstrated an even greater amount of growth retardation compared to controls. Normoxic embryos both (A) Normox/Flox and (B) Normox/Cre displayed normal morphology and growth. The hypoxic embryos (C) Hypox/Flox and (D) Hypox/Cre were significantly growth retarded, however there was no difference between Hypox/Flox and Hypox/Cre embryos. Scale bar is 1 mm. Reprinted with authors’ permission from Wendler CC et al. BMC Dev Biol 10:57; Copyright c 2010 Wendler et al.
