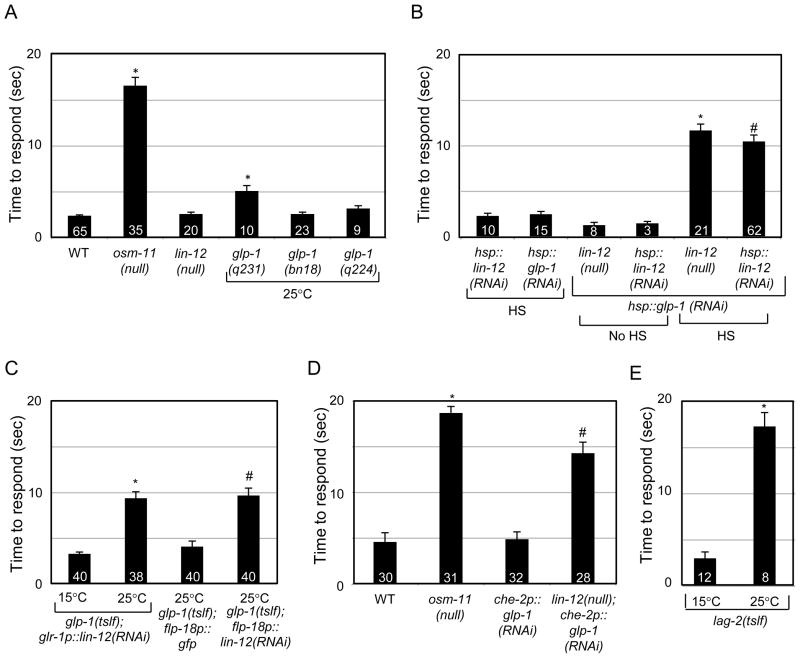
Figure 2.
C. elegans Notch receptors and DSL ligand are required for normal octanol response. (A) Decreasing function of either Notch receptor gene alone does not dramatically impair octanol response. *p<10−11 vs. wild type (WT). (B) Knockdown of both Notch receptors impairs octanol response in adult animals #p<0.05 vs. hsp::lin-12(RNAi) HS, *p<0.05 vs. lin-12(null). (C) Notch receptors are required in neurons. lin-12 function is required in a subset of interneurons for normal octanol response. lin-12(RNAi) in glr-1 and flp-18-expressing neurons impairs octanol response. *p<10−11 vs. animals at 15°C. #p<10−4 vs. glp-1(tslf);flp-18p::gfp. (D) glp-1 functions in ciliated sensory neurons to regulate octanol response. glp-1(RNAi) in che-2-expressing ciliated sensory neurons impairs octanol response in lin-12(null) animals. *p<10−12 vs. WT; #p<10−8 vs. che-2p::glp-1(RNAi). (E) lag-2 function is required in adult animals for octanol response. *p<10−7. See Supplemental Methods 2 for details.