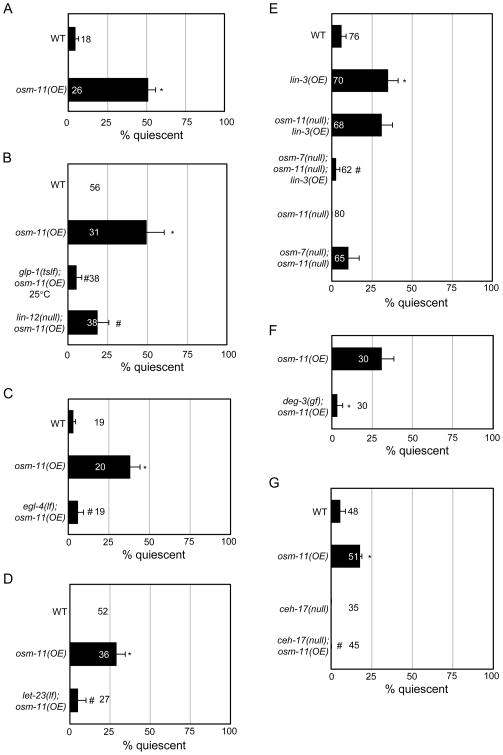
Figure 3.
OSM-11 over-expression induces quiescence in adults. In all panels, osm-11 was expressed under the heat shock promoter (hsp::osm-11). (A) OSM-11 over-expression (OE) induces spontaneous, transient and anachronistic quiescence in adult animals. *p<10−5 vs. WT. (B) osm-11(OE)-induced adult quiescence requires Notch receptor function. glp-1(tslf) or lin-12(null) suppress osm-11(OE) induced quiescence. *p<0.05 vs. WT; #p<0.05 vs. osm-11(OE). (C) OSM-11 over-expression induced quiescence is suppressed by egl-4 (lf). *p<0.0001 vs. wild type (WT); #p<0.05 vs. osm-11(OE). (D) Loss of LET-23 EGF receptor function (let-23(lf)) suppresses osm-11(OE)-induced quiescence. *p<0.001 vs. WT; #p<0.05 vs. osm-11(OE). (E) Simultaneous loss of osm-7 and osm-11 suppresses LIN-3 EGF over-expression (lin-3(OE))-induced adult quiescence. *p<0.01 vs. WT; #p<0.05 vs. lin-3(OE). (F) deg-3-induced neurodegeneration suppresses osm-11(OE)-induced quiescence. *p<0.05. As the locomotion of deg-3(u662) animals is severely uncoordinated, pharyngeal pumping was used to assess quiescence. (G) Defective axon outgrowth in ceh-17-expressing neurons suppresses osm-11(OE)-induced quiescence. ceh-17(null) affects processes of ALA and a subset of other neurons. *p<0.05 vs. WT; #p<0.001 vs. osm-11(OE). See Supplemental Methods 3 for details.