Figure 3. Effects of 5-HT1AR stimulation on L-DOPA-related striatal glutamate and AIMs in 6-OHDA- and sham-lesioned rats.
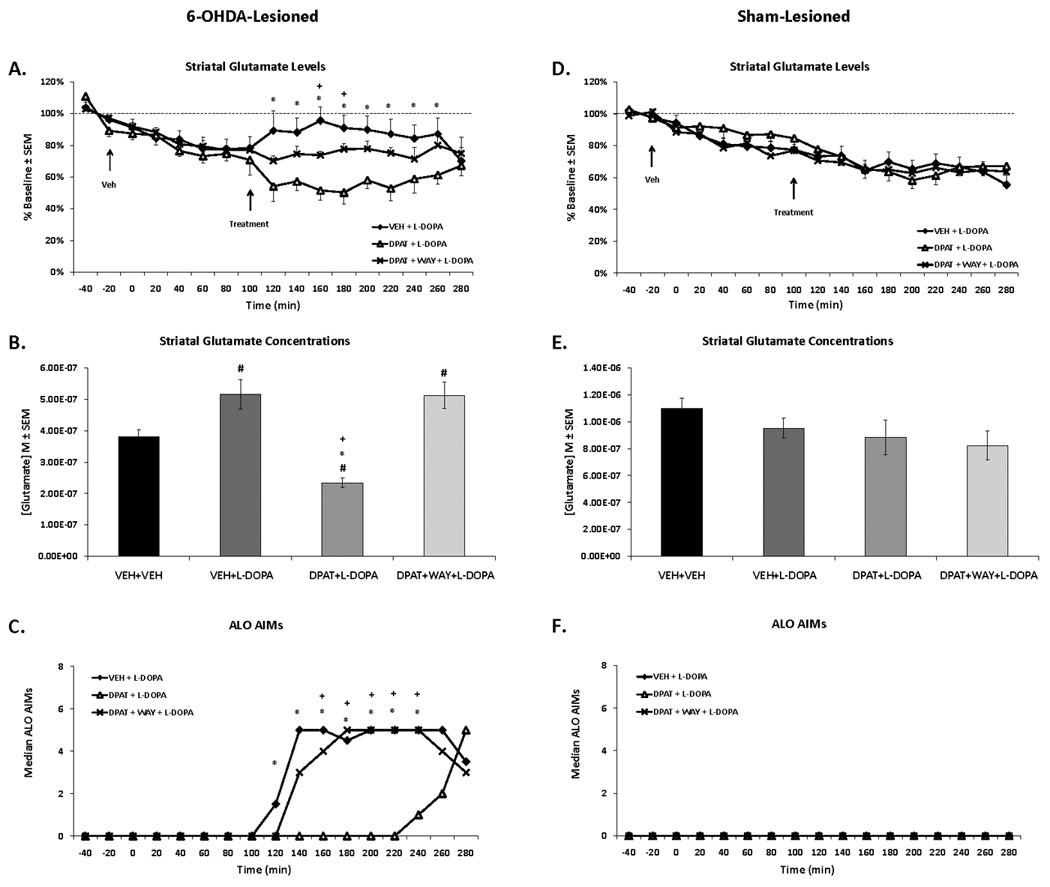
Rats in the first experiment received unilateral 6-OHDA or sham lesions of the MFB and 3 weeks later were primed with L-DOPA (12 mg/kg + benserazide, 15 mg/kg, sc) once daily for 7 d. Dyskinetic (n=12) and sham-lesioned rats (n=11) underwent a microdialysis procedure including: 40 min baseline, 120 min vehicle treatment, 120 min drug treatment, and 60 min post-drug treatment sampling (dialysate collected every 20 min). Drug treatment included: Vehicle (VEH; 0.9% NaCl), the full 5-HT1AR agonist ±8-OH-DPAT (DPAT; 1.0 mg/kg, sc), or combined DPAT + the 5-HT1AR antagonist WAY100635 (WAY; 0.5 mg/kg, sc), immediately followed by L-DOPA (12 mg/kg, + benserazide, 15 mg/kg, sc). AIMs were observed during this time. Lines depict the means ± SEM of striatal glutamate (percent baseline) (A) and AIMs (C) for VEH+L-DOPA (n=8), DPAT+L-DOPA (n=7), and DPAT+WAY+L-DOPA (n=5) in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Results for sham-lesioned rats receiving VEH+L-DOPA (n=7), DPAT+L-DOPA (n=6), and DPAT+WAY+L-DOPA (n=6) are expressed in (D) and (F). Bars depict the means ± SEM concentrations of striatal glutamate (M) during the 120 min of vehicle (VEH+VEH) and 120 min of drug treatments in 6-OHDA- (B) and sham-lesioned (E) rats. Effects over time were determined by two-way mixed design ANOVAs for striatal glutamate (% baseline). Striatal glutamate concentrations (M) were analyzed with one-way ANOVAs. Treatment effects for AIMs (expressed as medians) were analyzed by employing non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis tests. Significant differences between treatments were determined by Mann-Whitney post hoc comparisons for AIMs and planned comparison tests for striatal glutamate (% baseline and M).
* p < 0.05 for VEH + L-DOPA vs DPAT + L-DOPA
+ p < 0.05 for DPAT + L-DOPA vs DPAT + WAY + L-DOPA
# p < 0.05 vs VEH + VEH (bar graph)
