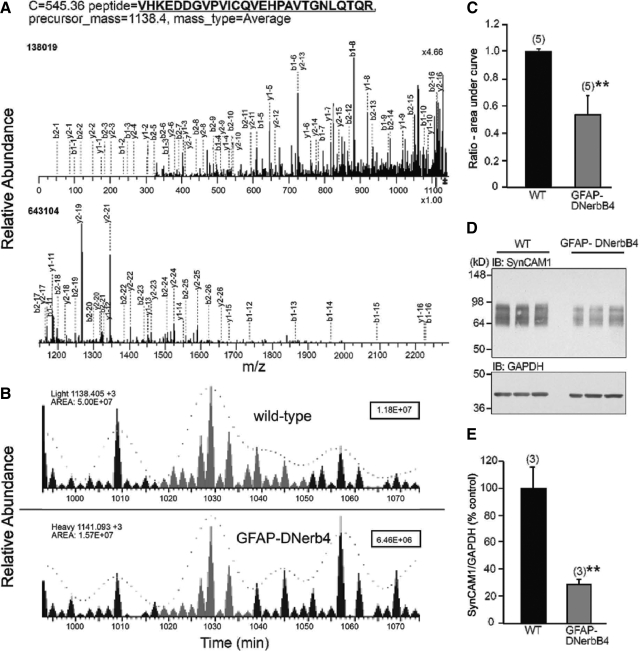
Fig. 1.
The abundance of SynCAM1 is reduced in the POA of immature mice with disrupted astrocytic erbB4 receptor signaling (GFAP-DNerbB4), as assessed by ICAT-μLC-MS/MS and Western blot. Peptides from the POA of WT and GFAP-DNerbB4 mice were labeled with the light and heavy form of the ICAT reagent, respectively. A, A representative mass chromatogram of the sequencing of one of the SynCAM1 peptide pairs detected using tandem mass spectrometry. The selected peptides were fragmented using CID, and the resultant C-terminus (b3, y1) and N-terminus (b1, y3) ions are displayed. B, Reconstructed single ion chromatograms of the isotopically light (WT) and heavy (GFAP-DNerbB4) SynCAM1 peptide partners, created by plotting the intensity of the signal observed at the relevant m/z value (light, 1138.405; heavy 1141.093) as a function of retention time (minutes). The area under the curve fitted to the SynCAM1 peptide ions pairs was greatly reduced in the GFAP-DNerbB4 samples compared with wild-type (WT: 5.00E+07; GFAP-DNerbB4: 1.57E+07). The numbers in the upper right-hand corner represent the scale of each chromatogram. C, Heavy to light ratio of five SynCAM1 peptides sequenced from WT (light) and GFAP-DNerbB4 (heavy) samples (measured by the area under the curve on the chromatogram using the INTERACT software package) shows erbB4-dependent SynCAM1 expression. **, P < 0.02 vs. WT animals. D, Decreased SynCAM1 protein levels in the POA of 30-d-old female GFAP-DNerbB4 mice as determined by Western blot analysis using antibody 3E1 (25 μg of protein per lane). E, Densitometric analysis of the SynCAM1 signal shown in D. **, P < 0.02 vs. WT animals. Numbers in parentheses above bars represent the number of independent observations per group, and vertical lines are sem.