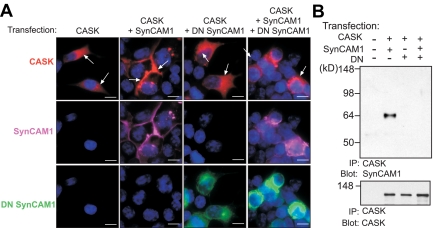
Fig. 6.
DN SynCAM1 inhibits SynCAM1 function by preventing SynCAM1 association to, and the cellular redistribution of, the scaffold, actin-binding protein CASK. A, left panels, Human embryonic kidney 293T cells transfected with a CASK-RFP expression plasmid show a cytoplasmic CASK localization (red). Left middle panels, Cotransfection of CASK-RFP with WT SynCAM1 results in CASK recruitment to the plasma membrane were SynCAM1 is localized (purple). Right middle panels, Cotransfection of DN SynCAM1 with CASK-RFP does not affect the cytoplasmic localization of the CASK protein (red), despite the presence of DN SynCAM1 (green) at the plasma membrane. Right panel, DN SynCAM1 prevents the SynCAM1-dependent recruitment of CASK-RFP to the plasma membrane. B, DN SynCAM1 prevents the association of WT SynCAM1 to CASK-RFP as assessed by coimmunoprecipitation assay of protein extracts from 293T cells transfected with CASK-RFP, WT SynCAM1, and DN SynCAM1. The proteins were immunoprecipitated with CASK antibodies and blotted with SynCAM1 monoclonal antibodies. To confirm CASK pulldown, the membrane was reprobed with CASK antibodies (lower panel in B). Bars, 10 μm. Cell nuclei (blue) are stained with Hoechst.