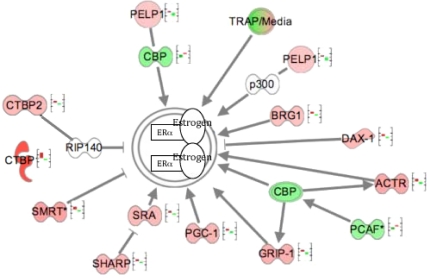
Fig. 4.
Regulation of the estrogen signaling pathway inside the nucleus. The figure displays gene expression of cofactors that modulate the ER + estrogen complex inside the nucleus. The first bar, from left to right, represents the fluorescent expression of a particular gene in MSEn, and the second bar in the graph represents PCOScc. Genes represented in red are up-regulated, and genes represented in green are down-regulated in PCOScc relative to MSEn. These values were obtained from the microarray analysis and exported to IPA. Note that each gene represented in the MSEn has the opposite expression in the PCOScc. The genes represented with a graph bar are those that reached a P < 0.05. Among the coactivators are: glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1); cAMP-response element binding protein (CBP/p300); thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex component (TRAP220); peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1 (PGC-1); nuclear receptor coactivator 3 (ACTR); SWItch/Sucrose NonFermentable-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 (BRG1); E1A binding protein p300 (p300) and K (lysine) acetyltransferase 2B (PCAF); proline glutamate and leucine rich protein 1 (PELP1); and steroid receptor RNA activator (SRA). Several corepressors regulate the activity of ERα either directly or via inhibiting a coactivator. Examples of direct inhibition include receptor-interacting protein (RIP140), silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid receptors (SMRT), and nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 1 (DAX-1). Corepressors of ER that inhibit indirectly include SMRT/HDAC1 associated repressor protein (SHARP) and C-terminal binding protein 2 (CTBP2).