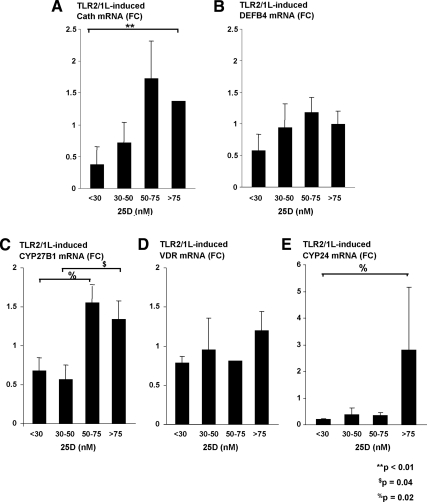
Fig. 3.
TLR2/1L induction of the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway in monocytes is also perturbed in the presence of vitamin D insufficiency. Primary human monocytes were then stimulated with a TLR2/1L for 24 h in 10% cord blood plasma of the same varying vitamin D concentrations as described in Fig. 2. Cathelicidin, DEFB4, CYP27B1, VDR, and CYP24 gene expression were again determined by qPCR (mean fold change ± sem). A, Cathelicidin gene expression was notably diminished in adherent cells cultured with severely vitamin D-deficient plasma samples vs. vitamin D-sufficient ones (P < 0.01). B, No difference was detected in DEFB4 expression after stimulation with a TLR2/1L when compared with cord blood 25(OH)D concentrations of the plasma. C, CYP27B1 gene expression was notably less in monocytes cultured in plasma with 25(OH)D below 50 nm. D, There were no differences in VDR gene expression after stimulation with the TLR2L. E, There was a greater induction of CYP24 gene expression in the monocytes cultured with vitamin D-sufficient plasma as previously described with CYP24 gene expression after TLR4L stimulation (P = 0.02).