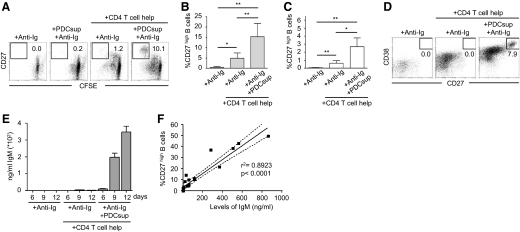
Figure 2. PDCs enhance naive B cell differentiation into IgM-secreting plasmablasts.
(A) Naïve B cells were stimulated with anti-Ig and PDC supernatants in the presence or absence of T cell help. Differentiation to CD27high plasmablasts was measured by flow cytometry. Gate numbers indicate percentage of CFSE low B cells that show high expression of CD27 after exclusion of dead cells and T cells. (B and C) Graphs show compiled data on the frequencies of CD27high B cells after culture with supernatants from TLR7/8 ligand-stimulated PDCs (B; n=6) or CpG A-stimulated PDCs (C; n=8). Data indicate mean ± sd. (D) Anti-Ig and PDC supernatants were added to naïve B cells in the presence or absence of T cell help. Differentiation to express high levels of CD27 and CD38 was assessed by flow cytometry. Gate numbers indicate percentage of cells that show high expression of CD27 and CD38. (E) Naïve B cells were cultured in the presence or absence of T cell help for 6, 9, or 12 days in parallel cultures with addition of anti-Ig and supernatants from TLR-stimulated PDCs. IgM production was measured in the culture supernatants using ELISA. Data from one representative donor are shown. (F) IgM levels from different stimulations were compared with the frequencies of CD27high B cells in the respective samples at Day 6. The 95% confidence interval is shown; P < 0.0001.