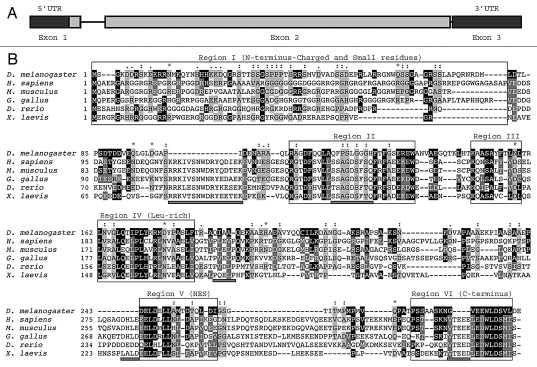
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic structure of the dAven gene. The three predicted exons of dAven are represented by rectangles connected by lines representing introns. The first exon includes a 95-bp 5′-UTR (untranslated region; dark grey) and a 885-bp coding region (light grey), whereas the rest of the coding sequence is located within the second exon (grey box). The third exon is composed of a 185-bp 3′-UTR (dark grey). (B) Alignment of the predicted dAven protein sequence and Aven proteins from various vertebrate species. The predicted amino acid sequence of dAven (AY071046) was manually aligned with those of Aven proteins of human (NP_065104.1), mouse (NP_083120), bird (NP_001005791), frog (NP_001090621) and fish (NP_001038757) origins. Identical residues (white letters in black boxes) and highly conserved residues (white letters in dark grey boxes) in dAven that are conserved in at least two other species are highlighted. Other conserved residues are shown in black letters and a light grey box. (:) indicates small residues (G, A, S, P, T, D, N); (.) indicates charged residues (K, R, D, E, H); and (*) indicates polar residues (K, R, D, E, N, Q).