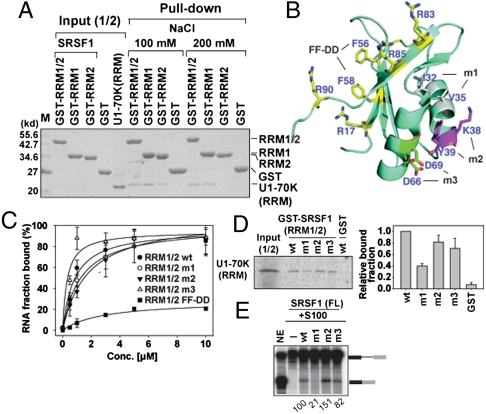
Fig. 4.
Two opposite surfaces of SRSF1 (RRMs) recruit ESE and U1-70K (RRM). (A) GST pull-down assay between GST-SRSF1 RRM1/2, RRM1, and RRM2 of 10 μg and U1-70K RRM (59–215) of 10 μg. (B) Ribbon presentation of SRSF1 (RRM1) (PDB ID code 1X4A). Putative RNA binding residues are denoted by yellow color. Residues in each mutant m1 (I32A/V35A), m2 (K38A/Y39A), and m3 (D68A/D69A) are denoted in three colors. (C) Ron ESE bindings to SRSF1 (RRM1/2) WT, m1, m2, m3, and FF-DD mutants (F56D/F58D) were measured by filter binding assay with error bars (SD) from three independent experiments. (D) Autoradiograph of GST pull-down assay between WT and mutants GST-SRSF1 (RRM1/2), and in vitro translated [35S]-met labeled U1-70K (RRM). The binding fraction of the U1-70K (RRM) to WT and mutants GST-SRSF1 (RRM1/2) were quantitated from three independent experiments. (E) In vitro splicing of β-gb pre-mRNA in S100 complementation assay using WT and mutants SRSF1 (FL) and relative splicing efficiency is quantified as shown.