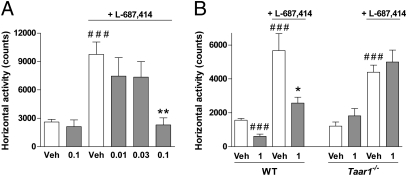
Fig. 6.
RO5166017 dose-dependently blocks L-687,414–induced hyperlocomotion. (A) In NMRI mice, RO5166017 administered orally dose-dependently blocked hyperlocomotion triggered by L-687,414 (50 mg/kg s.c.). ###P < 0.001 vs. saline/Veh; **P < 0.01 vs. L-687,414/Veh. L-687,414/RO5166017 (0.1 mg/kg) does not differ from groups without L-687,414 (n = 7–8 per group). (B) In Taar1−/− C57BL/6 mice but not in WT littermates, RO5166017 failed to antagonize hyperlocomotion triggered by L-687,414 (75 mg/kg s.c.). ###P < 0.001 vs. saline/Veh; *P < 0.05 vs. L-687,414/Veh (n = 6–8 per group). Numbers on the x axes are oral doses of RO5166017 in mg/kg. Veh, vehicle. Data represent the mean ± SEM.