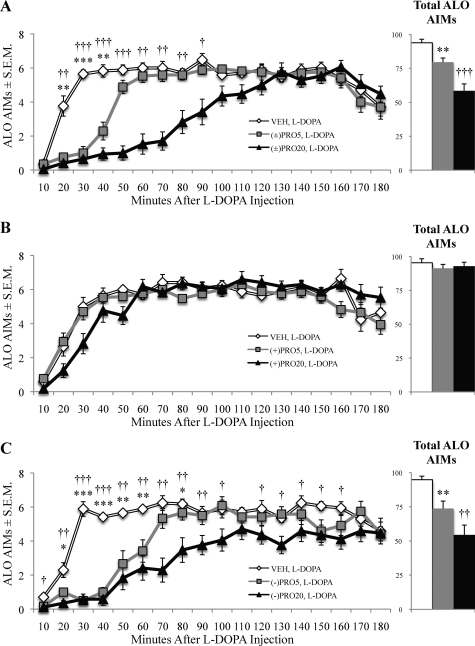
Fig. 4.
Propranolol dose-dependently and stereospecifically reduced the expression of ALO AIMs induced by l-DOPA. l-DOPA-primed hemiparkinsonian rats (n = 17) were given injections of racemic (±), levo (−), and dextro (+) propranolol (VEH, 5 or 20 mg/kg) 5 min before l-DOPA (12 mg/kg) in a within-subjects design. ALO AIMs were subsequently monitored. Symbols on main chart represent the treatment group time point mean ALO AIMs ± S.E.M. for (±)propranolol (A), (+)propranolol (B), and (−)propranolol (C). Bars on inlaid figure denote total ALO AIMs ± S.E.M. of treatment groups. Data were analyzed using the Friedman test with Wilcoxon signed-rank post hoc tests. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001 VEH versus PRO5; †, p < 0.05, ††, p < 0.01, †††, p < 0.001 VEH versus PRO20.