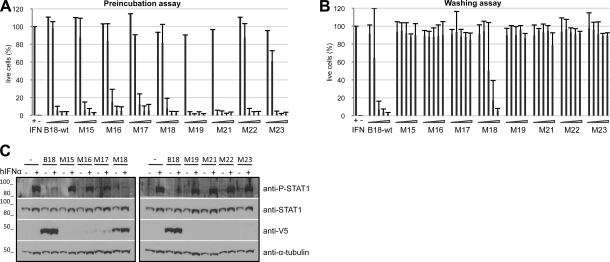
Figure 5.
IFN-binding and -blocking activities of B18 and mutant proteins. A) Preincubation assay, in which increasing amounts of supernatants containing the recombinant proteins (0.078–1.25 μl) were preincubated with 50 U of type I IFN, and the mixture was added to HeLa cells. After 16 h of incubation, cells were infected with VSV, and cell viability was determined after 72 h. Controls of treated (+IFN) and untreated (−IFN) cells are indicated. Data are means ± sd of >3 independent experiments done in triplicate. B) Determination of the inhibition of type I IFN antiviral activity by B18 protein and mutants at the cell surface in a wash assay. HeLa cells were incubated with increasing volumes (2.5–40 μl) of supernatants containing the indicated recombinant proteins for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were washed, and 50 U of type I IFN was subsequently added to HeLa cell monolayers. After 16 h incubation, cells were infected with VSV, and cell viability was determined after 72 h. Controls of treated and untreated cells are indicated. Data are means ± sd of >3 independent experiments done in triplicate. C) Inhibition of type I IFN-induced signaling by wild-type B18 and mutant proteins. HeLa cells were incubated with 40 μl of supernatants containing the corresponding proteins; after several washings, cells were left untreated (−) or exposed to 1000 U of hIFNα (+) for 30 min. Samples were analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are at left.