Figure 6.
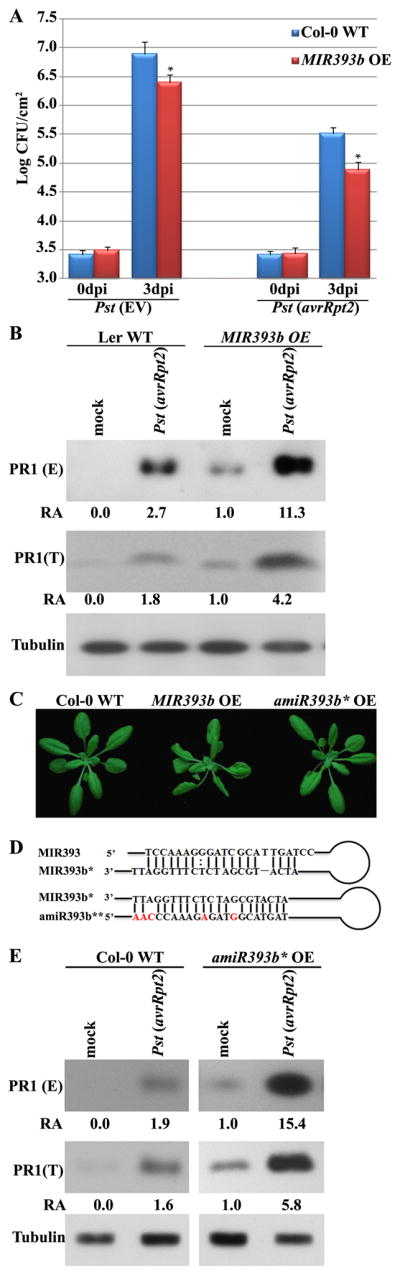
Overexpression of miR393b* resembles memb12-1 in disease resistance responses. (A) MIR393b overexpression plants (MIR393b OE) were more susceptible to both Pst (EV) and Pst (avrRpt2) than WT plants. Pathogen growth was measured as in figure 1C. Error bars represent standard deviation of six leaf discs (*: p<0.05). Similar results were obtained from three biological replicates. (B) Overexpression of MIR393b promotes PR1 secretion. The level of PR1 was measured as in Fig. 4B. Three biological repeats yielded similar results. (C) Developmental phenotypes of transgenic plants overexpressing MIR393b (middle) and amiR393b* (amiR393b* OE, right). Pictures were taken from three-week-old plants. (D) Sequences of miR393/393b* and miR393b*/393b** for generating transgenic MIR393b and amiR393b* plants. The nucleotides that are different between miR393 and miR393b** are in red. (E) amiR393b* transgenic plants show enhanced PR1 secretion. Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. See figure S4 for the characterization of MIR393b and amiR393b* transgenic plants.
