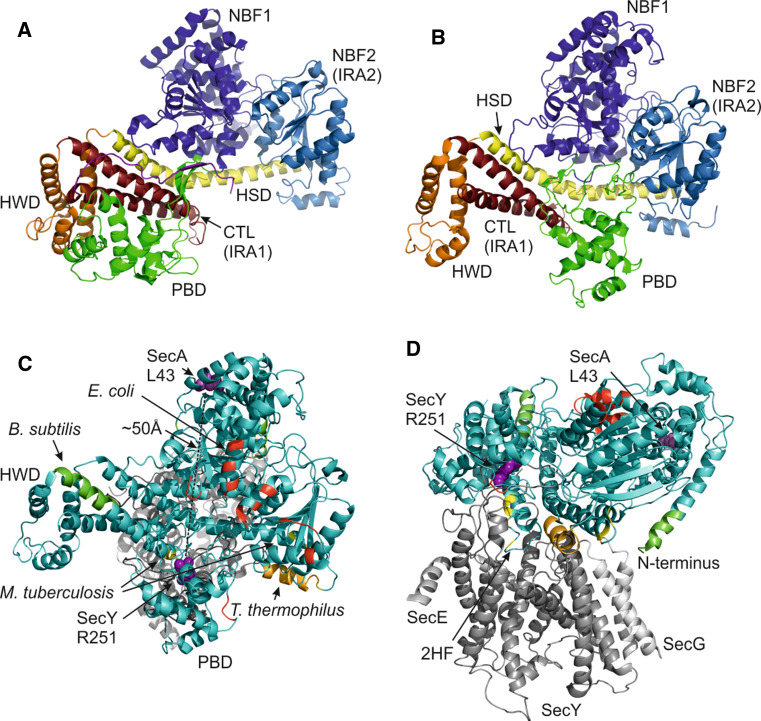
Fig. 2.
Conformational changes in SecA crystal structures and SecA dimerization interfaces. a SecA protomer from B. subtilis (1M6N). b SecA from T. maritima co-crystallized with SecYEG (not shown) (3DIN). c Top view (cytoplasmic side) of the SecA–SecYEG co-crystal as in (b) with residues implicated in dimerization in dimeric SecA structures of E. coli (red, 2FSF), B. subtilis (green, 1M6N), T. thermophilus (orange, 2IPC) and M. tuberculosis (yellow, 1NL3). Residues SecY251 and SecA43 that were previously crosslinked [26] are shown as purple spheres. SecA is displayed in cyan and SecYEG in gray. d Side view of (c)