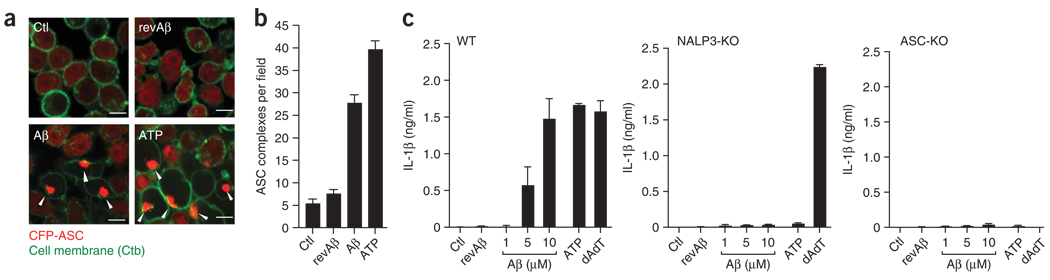
Figure 2.
Fibrillar Aβ activates the NALP3 inflammasome. (a) Confocal microscopy of wild-type immortalized microglial cells stably transduced with CFP-ASC, left unstimulated or stimulated for 4 h with revAβ (10 µM), Aβ (10 µM) or ATP (1 mM) in duplicate after being primed with LPS; cell membranes were stained with fluorescent choleratoxin subunit B (Ctb; green), and arrowheads indicate clusters of CFP-ASC (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. (b) Quantification of the images in a (mean and s.e.m. of five random fields). Data are representative of experiments done twice with nearly identical results. (c) ELISA of the release of IL-1β into the supernatants of LPS-primed bone marrow–derived wild-type, NALP3-deficient (NALP3-KO) and ASC-deficient (ASC-KO) macrophages left unstimulated or stimulated with Aβ (1, 5 or 10 µM), revAβ (10 µM) or ATP (5 mM) or transfected with poly(dA:dT) (200 ng) for 6 h. Data are representative of experiments done twice (error bars, s.e.m.).