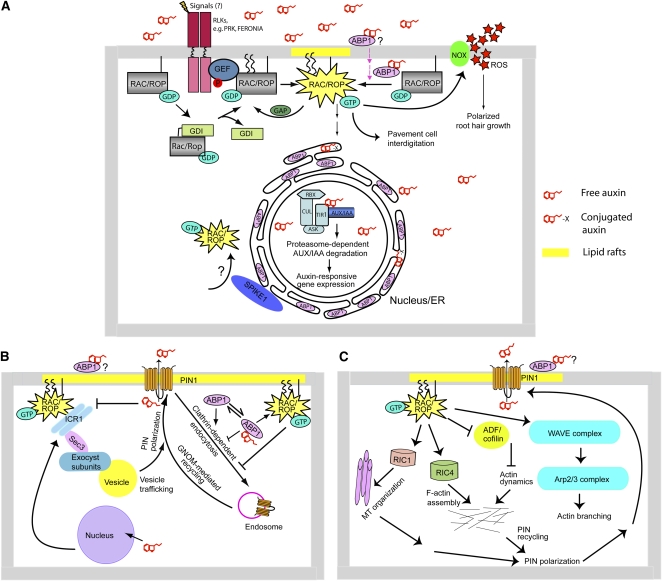
Figure 1.
Regulation of RAC/ROP Signaling and Its Downstream Pathways.
(A) Regulation of RAC/ROP cycling and downstream pathways. Only three cellular target systems are shown: auxin-responsive gene expression, control of polarized root hair growth, and regulation of pavement cell interdigitation. Potential SPIKE1-mediated intracellular RAC/ROP activation remains to be demonstrated. GDI is guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor. The straight line connecting RAC/ROP to the membrane represents modification by geranylgeranylation, and the two wavy lines represent S-acylation.
(B) Direct effect of RAC/ROPs on PIN polar localization. The model summarizes the involvement of the RAC/ROP effector ICR1 in recruitments of PIN to polar domain in the plasma membrane and the transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of ICR1 expression and stability by auxin. Where RAC/ROP and ABP1 may intersect in their regulation of PIN endocytosis is also depicted.
(C) Indirect effects of RAC/ROPs on polar PIN localization. The model shows how RAC/ROPs may modulate PIN localization indirectly through regulation of actin and microtubule cytoskeleton. MT, microtubule; ADF/cofilin, actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin; Arp2/3 complex, actin-related protein 2/3 complex, an actin-nucleating protein complex; WAVE complex, a protein complex that activates the Arp2/3 complex.