Figure 1.
Analysis of Arabidopsis Plants That Were Stably Transformed with GUN4-Derived Transgenes.
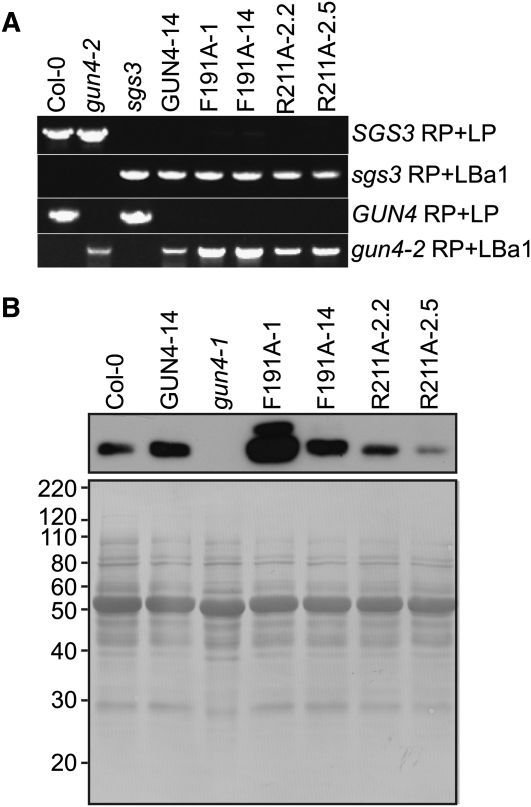
(A) Genotyping of the sgs3 and gun4-2 T-DNA insertion alleles in Arabidopsis plants that were stably transformed with GUN4-derived transgenes. Transgenic plants were homozygous for gun4-2, sgs3, the transgene indicated above lanes 4 to 8. Genomic DNA was extracted from the wild type (Col-0), the indicated mutant, or the indicated stably transformed line. Plants were screened for wild-type and T-DNA insertion alleles by PCR-based genotyping with oligonucleotides that can amplify PCR products from SGS3 (SGS3 RP + LP), GUN4 (GUN4 RP +LP), or particular T-DNA insertion alleles (sgs3 RP + LBa1 or gun4-2 RP + LBa1). PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis in agarose gels followed by staining with ethidium bromide.
(B) Analysis of GUN4 protein levels in Arabidopsis plants that are stably transformed with GUN4-derived transgenes. Transgenic plants were homozygous for gun4-2, sgs3, and the indicated transgene. Whole seedling extracts were prepared from the indicated mutant or the indicated stably transformed line grown in 100 μmol m−2 s−1 broad-spectrum white light. Aliquots of these whole seedling extracts that contained 10 μg of protein were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GUN4 antibodies (top panel) to detect the 22-kD band that corresponds to GUN4. After immunoblotting, the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane was stained with Coomassie blue (bottom panel). Mass standards are indicated at the left in kilodaltons.