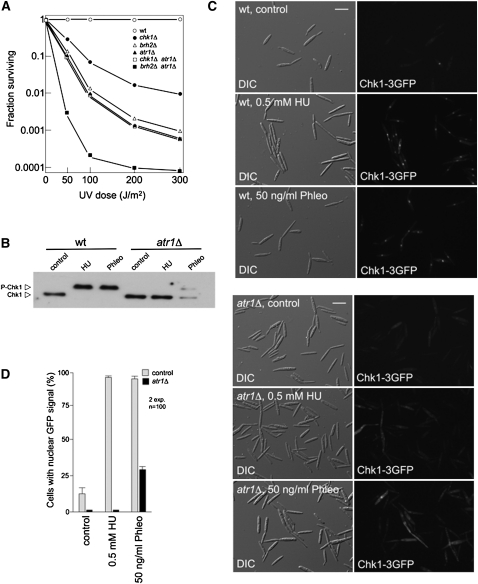
Figure 3.
Atr1 Is Required for Activation of Chk1 in Response to DNA Damage in U. maydis.
(A) Epistasis analysis between chk1, atr1, and brh2. Survival curves against UV irradiation of the indicated single and double mutants were obtained. Cells were grown to late log phase, adjusted to a density of 2 × 107 cells per mL, and irradiated with UV. Survival was determined by counting colonies visible after incubation for 2 to 3 d. wt, wild type.
(B) In vivo phosphorylation of Chk1 in response to agents that induce DNA damage depends on Atr1. Wild-type (UMP162) and atr1Δ (UMP207) cells carrying an endogenous Chk1-T7 allele were grown with no treatment (control) or in the presence of 0.5 mM HU or 50 ng/mL phleomycin (Phleo) for 6 h. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with a commercial anti-T7 antibody, and immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-T7 antibody.
(C) Atr1 is required to localize Chk1 at the nucleus. Cell images of wild-type (UMP111) and atr1Δ (UCS15) strains carrying a Chk1-3GFP fusion protein after 3 h of incubation in the presence of HU or phleomycin (Phleo). DIC, differential interference contrast. Bar = 10 μm.
(D) Quantification of the cell response to DNA damage as the percentage of cells carrying a clear nuclear GFP fluorescence signal. The graph shows the result from two independent experiments, counting more than 100 cells each. Means and sds are shown.