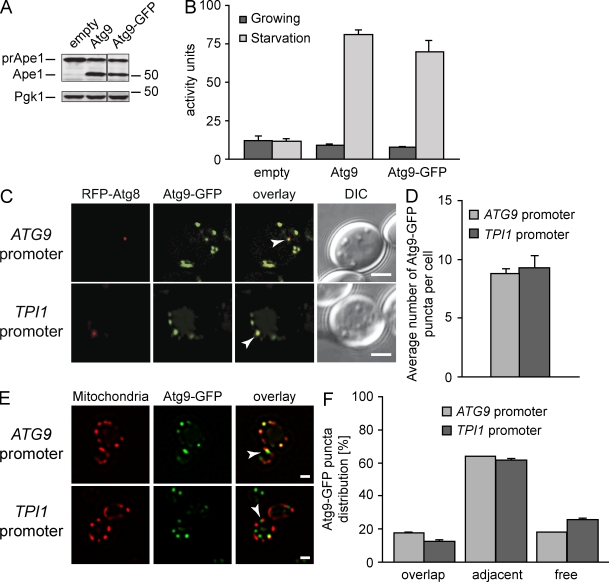
Figure 1.
The Atg9-GFP construct for IEM analyses. (A) The prApe1 processing is normal in Atg9-GFP–expressing cells. The atg9Δ (JCK007) mutant transformed with either an empty vector (pRS416), a plasmid carrying the ATG9 gene (pJK1-2416), or the ATG9-GFP fusion (pATG9GFP416) was grown in YPD medium to log phase before analyzing prApe1 maturation by immunoblotting. The cytosolic protein Pgk1 was used as a loading control. Mr is indicated in kilodaltons. The black line indicates that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (B) Autophagy is normal in the presence of Atg9-GFP. The atg9Δ (FRY300) cells expressing Pho8Δ60 and transformed with the same plasmids described in A were shifted from YPD medium (dark gray bars) to SD-N medium (light gray bars) for 4 h. Autophagy induction was determined by a Pho8 activity assay. (C and D) Atg9-GFP has a normal distribution, and one of the Atg9-GFP-containing puncta is the PAS. Strains expressing Atg9-GFP under the control of the ATG9 promoter (FRY162) or the TPI1 promoter (MMY067) were transformed with a plasmid (promRFPATG8415) carrying the PAS protein marker RFP-Atg8. (C) Transformants were cultured to log phase and imaged. The number of Atg9-GFP puncta per cell was counted (D) and error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Arrowheads highlight colocalizations. (E and F) Part of Atg9-GFP distributes to mitochondria. The strains analyzed in C were transformed with the pmitoDsRed415 plasmid expressing mitochondria-targeted RFP and imaged (E). Arrowheads highlight Atg9 puncta adjacent to mitochondria. Determination of Atg9-GFP puncta distribution on mitochondria (F) was determined as described in Materials and methods, and error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. DIC, differential interference contrast. Bar, 2 µm.