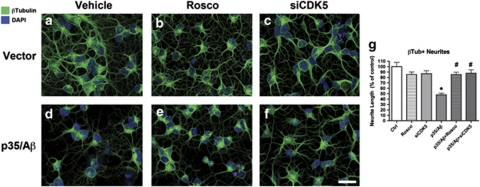
Figure 3.
Downmodulation of abnormal CDK5 activity in vitro rescues neuronal maturation. Differentiating NPCs were pretreated on day 2 with the pharmacological inhibitor Roscovitine (Rosco) or transfected with siRNA against CDK5 (siCDK5, 5 nM), and then infected 6 h later with adenovirus expressing p35, followed by treatment with Aβ on day 3 for 24 h. On day 4, NPC-derived neural progeny were briefly extracted and fixed with glutaraldehyde for β-tubulin immunofluorescence and neurite outgrowth analysis. Cell nuclei were co-stained with DAPI reagent. (a–c) Compared with controls (a), uninfected NPC-derived neural progeny treated with Rosco (b) or siCDK5 (c) showed only a mild reduction in the lengths of β-tubulin-positive neurites. (d–f) NPC-derived neural progeny with p35/Aβ treatment showed a notable decrease in the lengths of β-tubulin-positive neurites (d); this was rescued by treatment with Rosco (e) or siCDK5 (f). (g) Neurite outgrowth measurements using NeuronJ showed a 50% reduction in neurite lengths in p35/Aβ-treated cells, and this effect was reversed in cultures pretreated with Rosco or transfected with siCDK5. Scale bar=10 μm. *P<0.05 compared with vehicle-treated controls by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett's test (N=3). #P<0.05 compared with p35/Aβ-treated NPCs by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey–Kramer test (N=3)