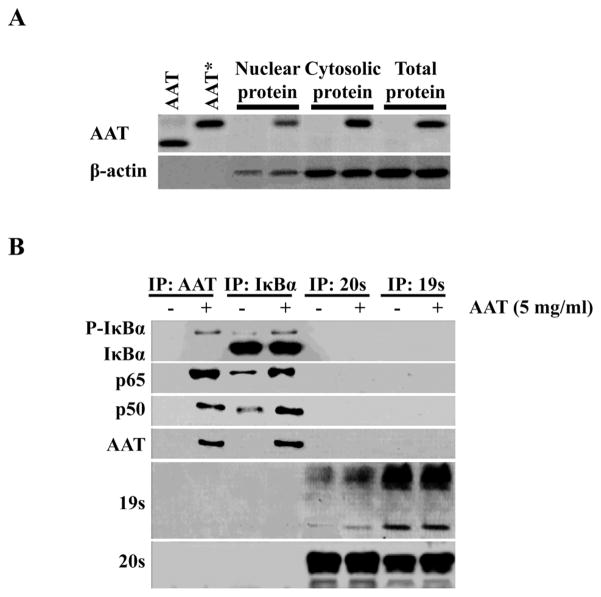
Figure 3.
AAT enters CD4+ T cells and associates with IκBα and NF-κB components p50 and p65 but not with the proteasome. CD4+ T cells were treated as in Figure 2. After 24 h of incubation with or without AAT (5 mg/ml), the nuclear, cytoplasmic and whole cell proteins were isolated and analyzed. (A) Isolated proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting for AAT. A β-actin immunoblot served as a protein loading control. As expected, β-actin was present in both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions (33–35). AAT and AAT* represent purified AAT and biotin-labeled purified AAT, respectively. (B) Isolated proteins from the cells were immunoprecipitated using Abs specific for I Ba, AAT, or the 19S or 20S proteasomal subunits. The data presented in these panels are representative of 3 independent experiments. The Abs used in immunoprecipitation are indicated at the top of panel B while those used in immunoblotting are indicated at the left of each blot. IP, Immunoprecipitation.