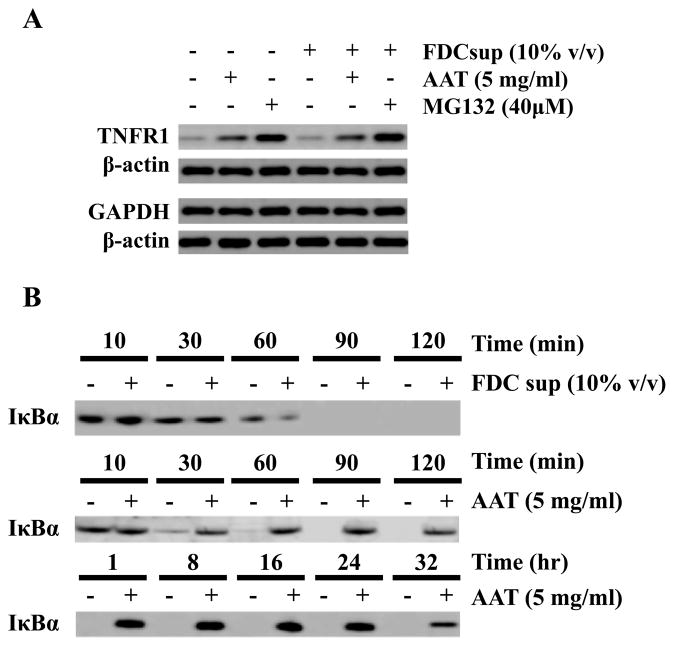
Figure 5.
AAT inhibits proteasomal degradation of TNFRI and increases IκBα half-life. (A) CD4+ T cells were isolated and infected as before and cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of FDC supernatant, AAT (5 mg/ml) and the proteasome inhibitor, MG132 (40 μM). After treatment, the cells were washed, lysed, and subjected to immunoblotting for TNFR1 (a protein degraded in the proteasome) or GAPDH (a protein degraded in the lysosome). β-actin was immunostained as a protein loading control. (B) The time-course of I Ba detection in infected CD4+ T cells was examined with or without FDC supernatant or AAT. Cells were cultured for 24 h with or without FDC supernatant or AAT (5 mg/ml) and then washed, pulsed for 10 min with 35S-Met (30 μCi/ml), washed and cultured (“chased”) with complete medium containing unlabeled Met. Samples were collected over a 2 h period when FDC supernatant was present or over a 32 h period when AAT (without FDC supernatant) was added. After culture, IκBα was immunoprecipitated and the resulting complexes were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Radiolabeled IκBα was detected using a phosphorimager. The data presented are representative of 3 independent experiments.