FIG 2 .
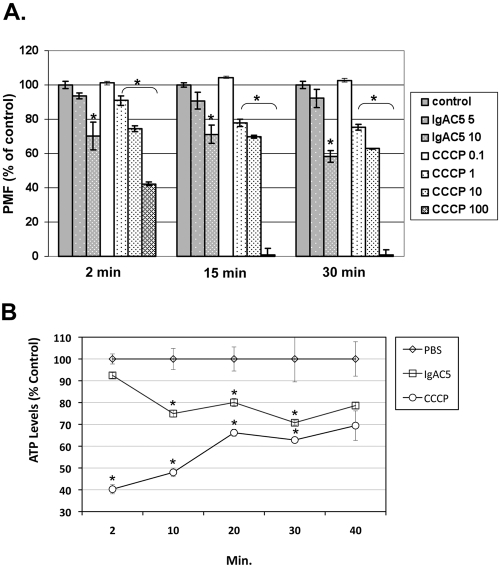
Reduction in S. flexneri membrane potential and ATP levels following IgAC5 treatment. (A) A total of 1 × 108 CFU of S. flexneri SJF31 per ml was loaded with the dye JC-1, seeded in 96-well microtiter plates, and then treated with indicated concentrations of IgAC5 (µg/ml) or CCCP (µM). At 2, 15, and 30 min following IgAC5 or CCCP treatment, the relative fluorescence emission signal ratios (530 nm/590 nm) were determined by using a Synergy HT (Bio-Tek, Winooski, VT) fluorescent plate reader with dual excitation (485/20 and 530/25) and dual emission (528/20 and 590/35). The fluorescence emission ratio of control cells was set to 100%. The results are the average values (with standard error) from a representative experiment done in triplicate. The asterisks indicate a significant (P < 0.05) reduction in membrane potential relative to the control samples, as determined by using the Student t test (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). SJF31 (ΔtolC::kan), an isogenic derivative of strain M90T, was created using λ red-mediated recombination with pKD4 as the antibiotic resistance marker template (26). It was necessary to use a TolC mutant for these studies to avoid rapid expulsion of JC-1 from the cell cytoplasm (24). (B) A total of 1 × 108 CFU of mid-log-phase S. flexneri strain M90T per ml grown in minimal medium with succinate (0.5%) as the sole carbon source was treated with a phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), IgAC5 (10 µg/ml), or CCCP (100 µM). At the indicated time points, total cellular ATP levels were measured with the BacTiter-Glo (Promega, Madison, WI) luminescence assay. The asterisks indicate significant (P < 0.05) reduction in ATP levels relative to the control samples, as determined by using the Student t test.