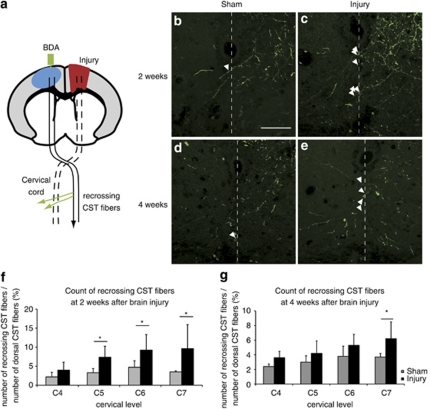
Figure 4.
Increased number of midline-crossing CST fibers in the cervical spinal cord after traumatic brain injury. (a) Illustration of midline-crossing (recrossing) CST fibers after cortical injury. BDA (green) was injected into the contralesional cortex (blue) to label the CST. The BDA-labeled CST fibers sprouted and recrossed to the denervated side of the cervical spinal cord after injury (green arrows). The recrossing fibers were counted from C4 to C7. (b–e) Photographs of recrossing CST fibers labeled with BDA (green) at the C7 level in the sham (b and d) and injured (c and e) mice at 2 (b and c) and 4 (d and e) weeks after the injury (Z stack, each 0.5 μm, by confocal laser-scanning microscopy). The recrossing CST fibers were marked with arrowheads. Scale bar: 50 μm. (f and g) Quantification of the recrossing CST fibers at each cervical level 2 (f) and 4 (g) weeks after the injury. The fibers increased in the injured group (black bars) compared with the sham group (gray bars). The data represent the mean±S.D. (2 weeks: sham n=6, injury n=4, 4 weeks: sham n=5, injury n=4); *P<0.05 (Mann–Whitney U-test)