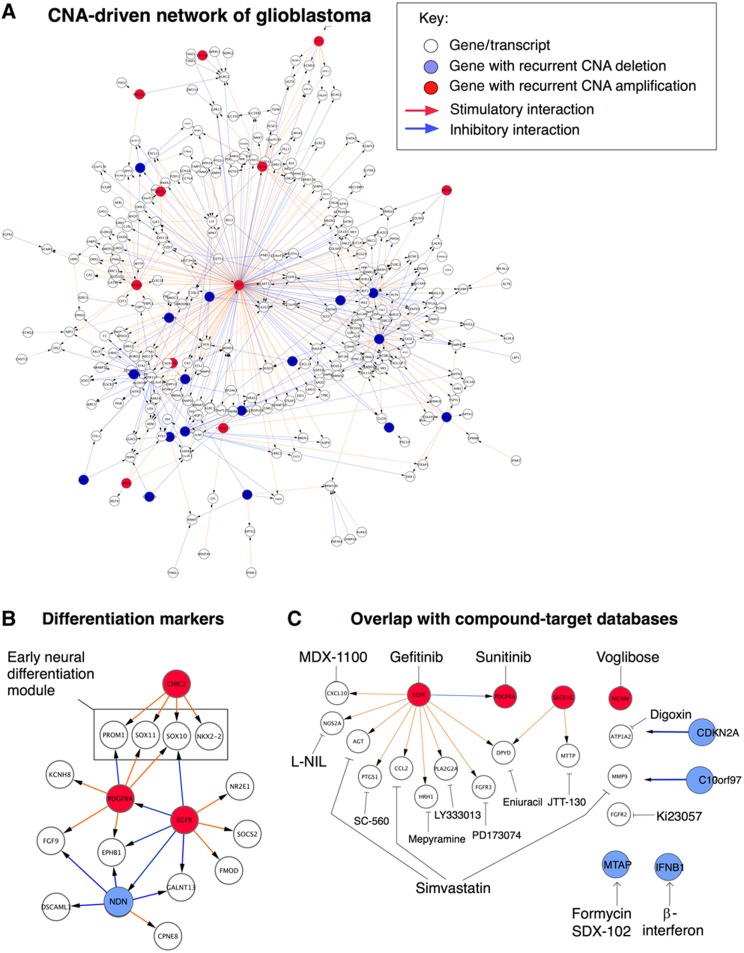
Figure 3.
CNA-driven network of glioblastoma. (A) Overall structure of the resulting glioblastoma network, defined as the set of interactions detected in at least 20% of the bootstrap networks (Figure 2B). Red arrows represent stimulatory interactions, blue arrows indicate inhibitory interactions. (B) Close-up of a network region containing early neural differentiation markers, including glioblastoma stem cell marker CD133/PROM1, under the control of hub genes CHIC2 and PDGFRA. The main hubs of the full network are listed in Table I. Note hub gene NDN, further analyzed in Figure 4. (C) Close-up of a network region containing genes that are targets of pharmaceutical compounds (as determined by searching the Ingenuity and Drugbank databases). Examples of compounds involved in links include simvastatin, SDX-102 (selectively active in MTAP-deficient tumors), PD173074 (a FGFR3 inhibitor), and cyclooxygenase 1 (COX1) inhibitors (PTGS1 encodes the COX1 protein).