Figure 6. Rtt107 contributes to spontaneous recombination events between sister chromatids.
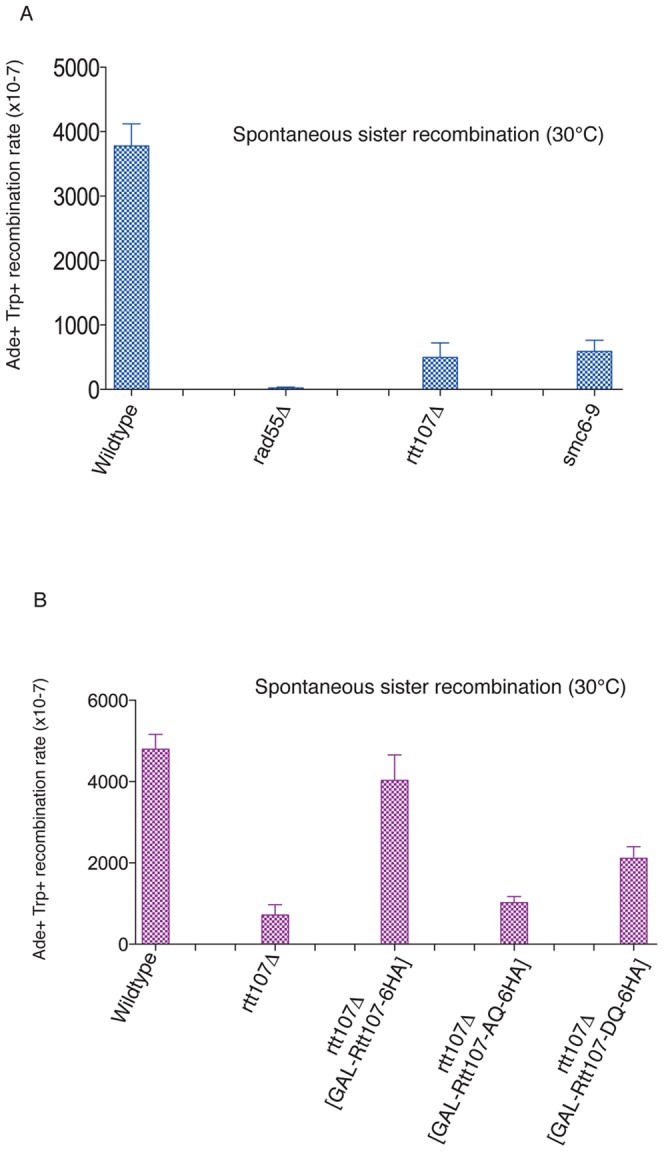
(A) The smc6–9 alele and rtt107Δ mutant show decreased recombination between sister chromatids. Wildtype (CCG7802), rad55Δ (CCG7804), rtt107Δ (CCG7855) and smc6–9 (CCG7856) strains carrying the ade2-TRP1-ade2 recombination assay [27] were grown on YPD plates at 30°C. Five independent colonies were inoculated into 5 ml of YPD and grown overnight at 30°C. Cells were pelleted and re-suspended in 1 ml of sterile water. Serial dilutions were then plated on SC medium minus adenine and tryptophan, and incubated for 3–4 days, after which colonies were counted. Ade+Trp+ recombination frequencies are plotted on the y-axis. (B) Rtt107 phosphorylation is required for its role in spontaneous sister chromatid recombination. Wt (CCG7802), rtt107Δ and rtt107Δ containing wildtype RTT107 (CCG8214), phospho-mutant RTT107-AQ (CCG8215) and phospho-mimmetic mutant RTT107-DQ (CCG8216) (under the galactose inducible promoter GAL1-10) strains with the engineered ade2-TRP1-ade2 recombination assay were grown on YPD plates at 30°C. Five independent colonies were inoculated into 5 ml of YPD and grown overnight at 30°C. Cells were then transferred to YP galactose and expression of constructs was induced for 4 hours. Cells were pelleted and re-suspended in 1 ml of sterile water. Serial dilutions were then plated on SC galactose medium minus adenine and tryptophan, and incubated for 3–4 days, after which colonies were counted. Ade+Trp+ recombination frequencies are plotted on the y-axis.
