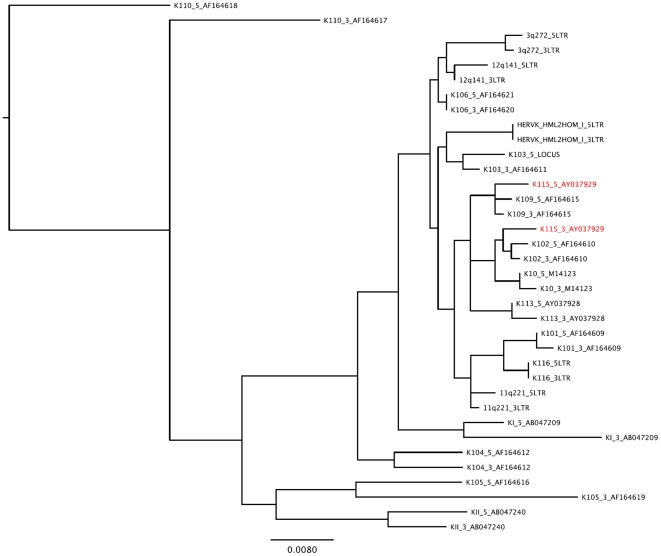
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of full-length HERV-K (HML-2) LTR sequences.
The clustering of the HERV-K 5′ and 3′ LTR sequences of each insertion suggests that gene conversion is rare in the HERV-K family. Each HERV is indicated by its name (K106 for HERV-K106). HERV taxa that may have undergone gene conversion are indicated in red. HERV-K115 5′LTR clusters with HERV-K109 suggesting a gene conversion occurred between these two HERV-K members. HERV-K10, HERV-K HML2HOM, and HERV-K110 are sometimes referred to as HERV-K107, HERV-K108, and HERV-K18, respectively. HERV-K110 was used to root the phylogeny because it is present in both Humans and Gorillas [16].