Figure 11.
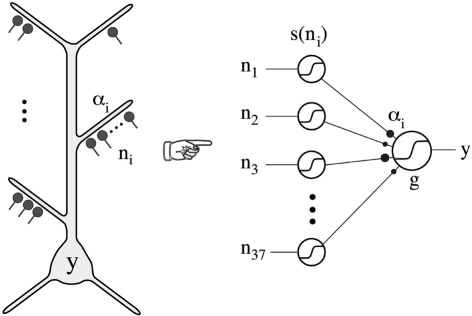
Thin oblique and terminal dendritic branches allow the pyramidal neuron to function as a two-layered neural network. The thin oblique and apical terminal dendritic branches constitute semi-independent local integrating subunits. Their interactions through the intervening dendritic tree can be regarded as constituting a second layer of neural network, in addition to the first layer formed by their interacting cell bodies and their axons. From Poirazi et al. (2003).