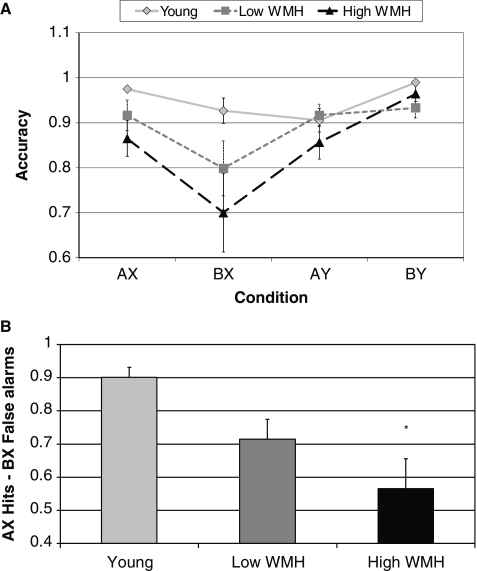
Figure 2.
(A) Accuracy for all conditions of the ‘AX’ continuous performance task; ‘AX’ and ‘BX’: older subjects with severe white matter hyperintensity (WMH) burden impaired relative to young group, P < 0.05. (B) Corrected recognition rate (‘AX’ hits − ‘BX’ false alarms) by group, differs from young, *P = 0.004. Low white matter hyperintensity denotes older subjects with minimal white matter hyperintensity, High white matter hyperintensity denotes older subjects with severe white matter hyperintensity.