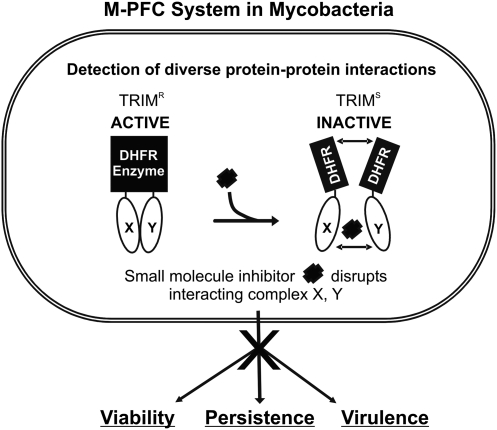
Fig. 1.
M-PFC in mycobacteria. Conceptual diagram of using M-PFC to search for inhibitors that can disrupt key mycobacterial protein interactions involved in essential, persistence, and virulence pathways. Black rectangles represent DHFR F(1,2) and F(3) fragments. X and Y are the translationally fused mycobacterial proteins selected for protein interaction studies with M-PFC and can include interactions involved in cell wall synthesis, two-component signaling, virulence, persistence, secretion, etc. A HTS platform based on M-PFC can detect small molecule inhibitors that disrupt the interaction between X and Y, which leads to an abolishment of downstream effects on viability, persistence, and virulence. HTS, high-throughput screen. DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; M-PFC, Mycobacterial–Protein Fragment Complementation.