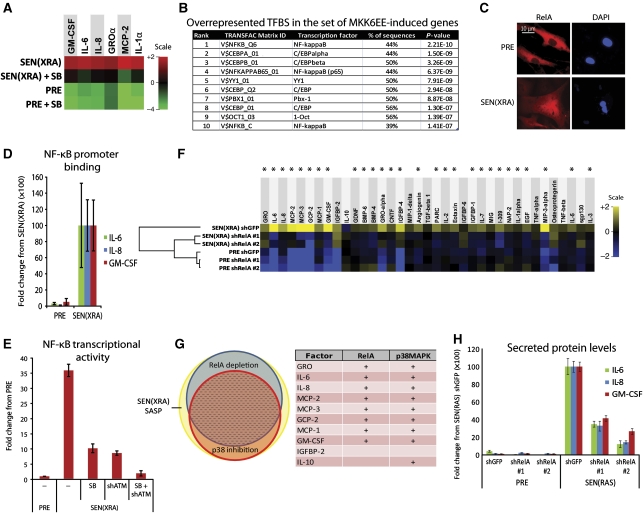
Figure 5.
p38MAPK induces SASP mRNAs by increasing NF-κB activity. (A) p38MAPK inhibition decreases SASP mRNA levels. Total RNA was extracted from PRE and SEN(XRA) HCA2 cells; mRNA levels for indicated genes were analysed by qRT–PCR. +SB: p38MAPK was inhibited with SB203580 for 48 h before sample collection. For each gene, the four signals were averaged to generate the baseline. Signals above baseline are red; signals below baseline are green. The heat map key shows log2-fold changes from baseline. p38MAPK inhibition significantly decreased (P<0.05) mRNA levels for all genes assayed. (B) Transcription factor (TF) binding sites (BS) in MKK6EE-induced genes. Genes encoding SASP proteins upregulated by MKK6EE expression (Figure 3C) were analysed for statistically overrepresented TFBS in the 200 bp upstream of the transcriptional start site. ‘% of sequences’ indicates percentage of sequences with ⩾1 binding site for each indicated weight matrix. TFBS are sorted by P-value. (C) RelA partially localizes to the nucleus during damage-induced senescence. PRE and SEN(XRA) cells were immunostained for RelA; representative images are shown. (D) Increased RelA binding to the promoters of SASP genes. Cells were irradiated, allowed to senesce (SEN(XRA)), and lysates were analysed by chromatin immunoprecipitation using an antibody against RelA. RelA binding to the promoters of the indicated genes is represented relative to Histone H3 binding and is normalized to SEN(XRA) binding for each gene. (E) p38MAPK inhibition and ATM depletion reduce NF-κB transcriptional activity in senescent cells. Cells were infected with lentivirus expressing an NF-κB luciferase reporter construct, irradiated, and allowed to senesce (SEN(XRA)). Cells were lysed and luciferase activity was measured. SB: p38MAPK was inhibited with SB203580 for 48 h before lysis. shATM: cells were infected with lentivirus expressing shRNA against ATM 5 days before lysis. (F) RelA depletion suppresses the SASP of SEN(XRA) cells. Cells were infected with lentivirus expressing either of two shRNAs against RelA (shRelA) or GFP (shGFP; control), selected, irradiated, and allowed to senesce (SEN(XRA)). Secreted proteins were detected by antibody arrays as in Figure 1. Shown are factors for which the SEN(XRA) level was significantly increased (P<0.05) over PRE. For each protein, the six signals were averaged to generate the baseline. Heat map and dendrogram were generated as in Figure 1E. Asterisks indicate factors that are significantly decreased by both RelA shRNAs (P<0.05). (G) Most p38MAPK-dependent SASP proteins are NF-κB dependent. Left: proportional Venn diagram displaying the overlap between p38MAPK-dependent factors (red), RelA-dependent factors (blue), and the SEN(XRA) SASP (yellow). In all, 76% of p38MAPK-dependent factors are also RelA-dependent (dashed area). Right: the 10 most upregulated SEN(XRA) SASP factors from Figure 1E. +: Proteins dependent on RelA or p38MAPK. (H) SEN(RAS)-induced IL-6, IL-8, and GM-CSF are RelA-dependent. Cells were infected with lentivirus expressing either of two shRNAs against RelA (shRelA) or GFP (shGFP; control) and selected. Cells were then infected with lentivirus lacking an insert (PRE) or expressing RASV12 and allowed to senesce (SEN(RAS)). CM were analysed by ELISA.