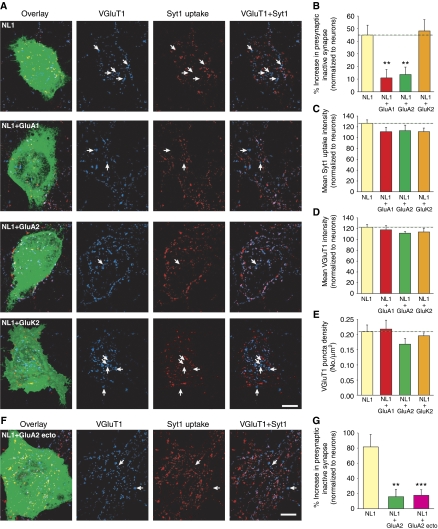
Figure 9.
Postsynaptic AMPARs participate directly in trans-synaptic retrograde signalling to influence glutamate release at a subset of presynaptic terminals. (A) Images of heterologous synapse formation between HEK293 cells and neurons. HEK293 cells were transfected with NL1 alone, or NL1 with either a GFP-tagged AMPAR subunit, GluA1 or GluA2, or a GFP-tagged kainate receptor subunit, GluK2 and co-plated with hippocampal neurons. Glutamatergic presynaptic terminals were identified by VGluT1 puncta (blue). Synaptic vesicle cycling at each terminal was measured by Syt1 antibody uptake (red). Functionally inactive presynaptic terminals were identified as VGluT1 puncta that lack Syt1 immunofluorescence (arrows). Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Quantification of functionally inactive presynaptic terminals. The fraction of inactive glutamatergic terminals on each HEK293 cell was calculated and normalized to the fraction of inactive terminals at neighbouring neuronal synapses (n=24–27 cells; **P<0.005). (C) Mean Syt1 uptake intensity at heterologous synapses (normalized to the mean Syt1 uptake intensity at neighbouring neuronal synapses; n=24–27 cells/group; P>0.05). (D) Mean VGluT1 puncta intensity at heterologous synapses (normalized to the VGluT1 intensity at neighbouring neuronal synapses, n=24–27 cells/group; P>0.05). (E) Density of glutamatergic synaptic contacts made onto HEK293 cells (n=24–27 cells/group; P>0.1). (F) Image of heterologous synapse formation on a HEK293 cell co-expressing NL1 and GluA2 ecto. Similar to (A), arrows indicate functionally inactive presynaptic terminals. Scale bar: 10 μm. (G) Quantification of functionally inactive presynaptic terminals formed on HEK293 cells expressing NL1 alone, NL1+GluA2, or NL1+GluA2 ecto (n=27–31; **P<0.005; ***P<0.001).