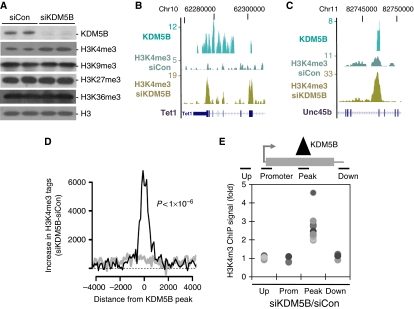
Figure 3.
KDM5B removes local domains of intragenic H3K4me3. (A) Immunoblot analysis of bulk histone modifications from ESCs transfected with control/KDM5B siRNAs. (B, C) Genome browser tracks depicting KDM5B ChIP-Seq peaks and H3K4me3 ChIP-Seq peaks from control (siCon) or KDM5B knockdown cells (siKDM5B). The numbers on the left axes indicate peak amplitude. (D) Histogram depicts the difference of H3K4me3 ChIP-Seq tag counts following knockdown of KDM5B (siKDM5B) versus control (siCon). ChIP-Seq tag counts are plotted relative to the centre of mass of KDM5B ChIP-Seq peaks (black line) or randomized controls (grey line). The ChIP-Seq difference was normalized by total tag counts and tags within 1.5 kb of RefSeq gene 5′ ends were not included. The difference of H3K4me3 ChIP-Seq tag counts following knockdown of KDM5B was highly significant (Wilcoxon rank-sum P<1 × 10−6). (E) Scatter plot depicts H3K4me3 ChIP data following KDM5B knockdown (siKDM5B) at KDM5B ChIP-Seq peaks (Peak), upstream regions (Up), associated promoters (Prom), and downstream regions (Down). Data are expressed as the ratio of H3K4me3 ChIP signal from siKDM5B over siCon. Each dot represents a distinct ChIP-Seq peak locus and all comparison to Peak data P<0.01.