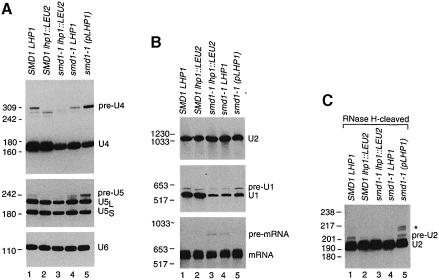
Fig. 2. The levels of 3′-extended U RNAs depend upon the amount of Lhp1p present. (A) RNA extracted from wild-type (lane 1), SMD1 lhp1::LEU2 (lane 2) and smd1–1 cells containing either no LHP1 (lane 3), chromosomal LHP1 (lane 4) or plasmid LHP1 (lane 5) was fractionated in denaturing gels and subjected to Northern analysis using oligonucleotides complementary to U4 (top), U5 (middle) or U6 (bottom panel). To visualize pre-U5 RNA, the autoradiograph was overexposed, making the difference in mature U5 levels between wild-type and smd1–1 lhp1::LEU2 cells less apparent. (B) RNA was fractionated as in (A) except that the gel was run to maximize resolution of larger RNAs. The blot was probed to detect U2 RNA (top panel), U1 RNA (middle panel) and CRY1 mRNA (bottom panel). (C) The RNA was subjected to oligonucleotide-directed RNase H cleavage to generate a 3′ fragment of U2 RNA of ∼195 nucleotides. Samples were analyzed by Northern blotting using an oligonucleotide complementary to the 3′ end of U2 RNA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.