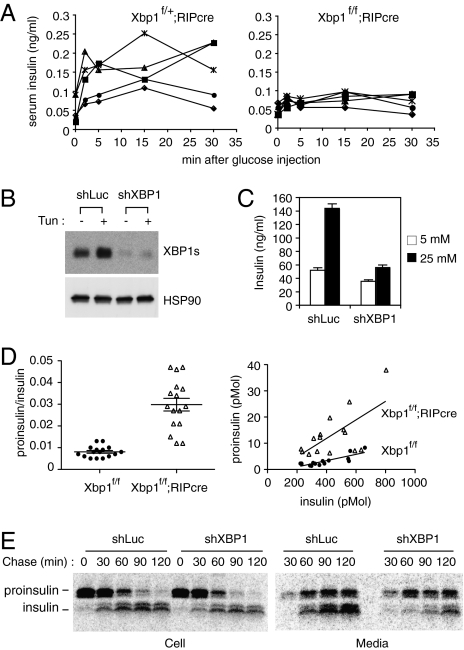
Fig. 3.
Impaired insulin secretion and proinsulin maturation in XBP1-deficient β-cells. (A) Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion assays. Serum insulin levels were measured in control heterozygous Xbp1f/+;RIP-cre and Xbp1f/f;RIP-cre mice at indicated time points after a bolus glucose injection. Each line represents an individual mouse. (B) Min6 cells stably expressing shRNAs targeting control luciferase or XBP1 mRNAs were tested for XBP1s expression by Western blot. (C) Cells were pretreated with 2.5 mM glucose for 2 h and then cultured in 5 mM or 25 mM glucose media for 2 h. Culture media were collected to measure insulin content by ELISA. (D) Serum proinsulin levels relative to total insulin in WT and Xbp1f/f;RIP-cre mice were determined. Data from both males and females were combined, because sex difference was not significant. The graphs display proinsulin:insulin ratio (Left) or proinsulin and insulin concentrations (pmol per liter) (Right). Each dot represents an individual mouse (4- to 6-mo-old). (E) Min6 cells expressing control or XBP1 shRNA were pulse-labeled for 30 min with [35S]Met/Cys and then cultured in chase media for the indicated time. Cells and culture supernatants were harvested for immunoprecipitation of radiolabeled insulin and proinsulin, which were revealed by SDS/PAGE followed by autoradiography.