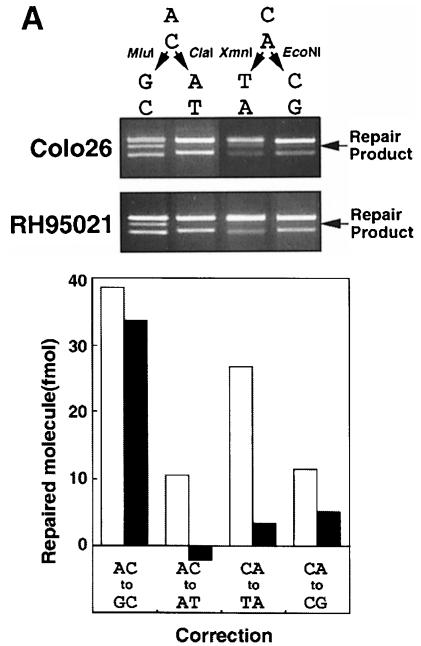
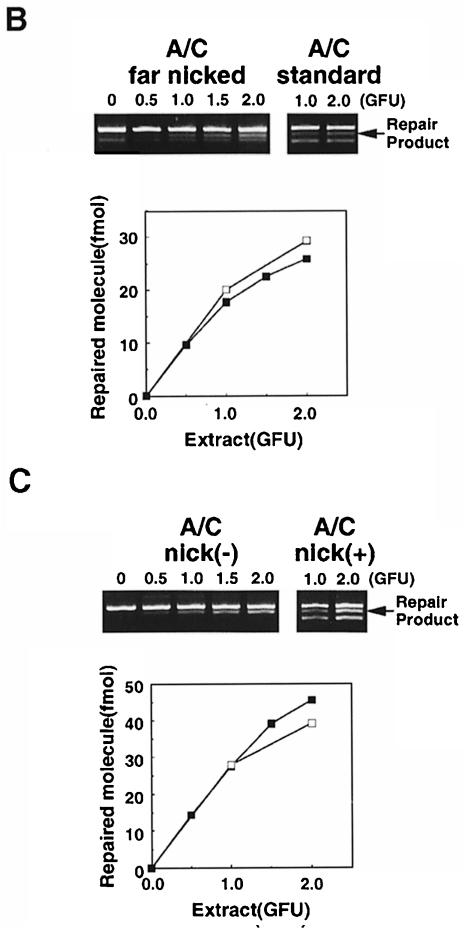
Fig. 6. Direction of correction and nick dependency of MSH2-independent A/C mismatch repair. (A) A/C and C/A mismatch correction by RH95021 and Colo26 cell extracts. Standard substrates containing an A/C or a C/A mispair were incubated with 1 GFU of either Colo26 or RH95021 extracts. The extent of correction to either G:C or A:T was examined. The diagnostic restriction enzymes for each correction event are indicated. Products were analysed and quantified and are expressed as the extent of correction in either direction. Colo26 (□); RH95021 (▪). (B) Effects on repair of the distance of the nick from the A/C mismatch. Repair assays were carried out using the amount of extract indicated. The standard substrate (A/C standard) contained the nick 580 bp 3′ to the mispair. In the ‘far nicked’ substrate, the nick is 1500 bp on the 5′ side of the mismatch. Following incubation with the amounts of RH95021 cell extract shown, repair was quantitated and is expressed as a function of extract concentration. ‘Far nicked’ substrate (▪); standard nicked substrate (□). (C) Nicked and ligated duplexes as substrates for A/C repair by RH95021 extracts. Repair assays were carried out using the amount of extract indicated. The standard substrate, A/C nick(+), contained a nick 580 bp 3′ to the A/C mispair. Nick(–) substrates were covalently closed duplexes in which the nick had been removed by ligation with T4 DNA ligase as described in Materials and methods. Following incubation with the amounts of RH95021 cell extract shown, repair was quantitated and is expressed as a function of extract concentration. Ligated substrate (▪); standard nicked substrate (□).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.