Fig. 7.
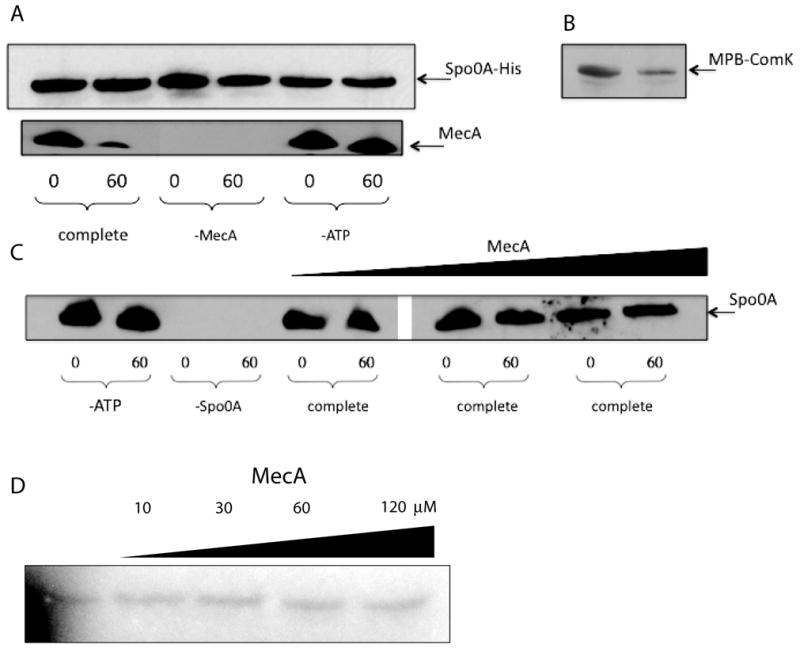
In vitro degradation assay. Spo0A-His, Spo0A, ComK-MBP and MecA were detected by immunoblotting with their cognate antisera. Samples were taken after zero and 60 minutes incubation. All incubation mixtures contained MecA, ClpC, ClpP, ATP and an ATP regenerating system unless otherwise indicated. (A) The incubation mixtures contained Spo0A-His. (B) The incubation mixture contained ComK-MBP, ClpC, ClpP, MecA and ATP. (C) Native Spo0A protein (0.3 μM) and ATP were included in these incubations, unless otherwise indicated and the concentration of MecA was varied in the 6 rightmost lanes (0.4 μM, 1.5 μM and 5 μM). Samples were run on the same gel, but an irrelevant portion was excised between lanes 6 and 7. (D) His-tagged KinA, Spo0F, Spo0B and untagged Spo0A (each at 0.2 μM) and various concentrations of MecA-His6 were incubated in the presence of 32P-γ-ATP as described in Experimental Procedures and following the published procedures (Fujita & Losick, 2003) and (Burbulys et al., 1991). The samples were autoradiographed after resolution by SDS-PAGE. Just before loading, bovine serum albumin was added to equalize the total protein loaded per lane. The gel was deliberately underexposed to ensure that the signals were within the sensitive range of film response. In control experiments, omission of the individual phosphorelay components prevented phosphorylation of Spo0A (not shown).
