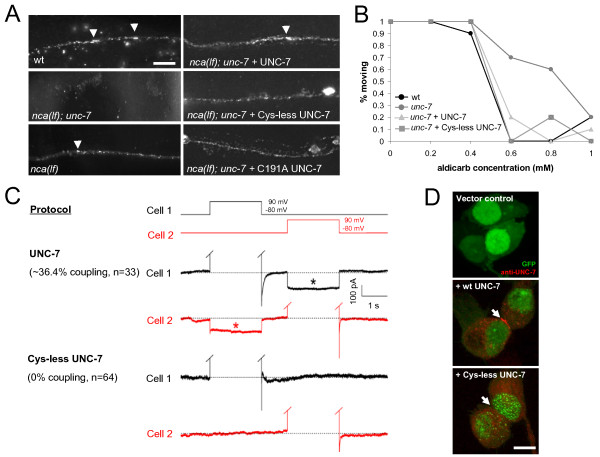
Figure 4.
Cys-less UNC-7 fails to localize to large junctional-like structures, but remains functional to rescue unc-7 aldicarb resistance. (A) Ventral nerve cord images of anti-UNC-7 immunostaining in wild type, nca(lf), nca(lf); unc-7 and nca(lf); unc-7 animals expressing wild type UNC-7 and mutant forms of UNC-7 under a pan-neuronal promoter (Prgef-1). Endogenous UNC-7 in wild type and nca(lf), as well as exogenously and pan-neuronally expressed UNC-7 in nca(lf); unc-7 all showed punctate distribution: bright and elongated patches resembling large junctional structures (arrowheads) and numerous dense punctate of unknown structures. Cys-less, or C191A UNC-7 eliminated these junctional-like patches, but left the smaller-sized densely populated punctate signal unchanged. Scale bar: 5 μm. (B) Representative results of same day experiments for aldicarb sensitivity after 240 min of exposure to aldicarb (n = 10). unc-7(hp121) mutants had increased aldicarb resistance when compared to wild type animals. Expression of either UNC-7 or Cys-less UNC-7 restored aldicarb sensitivity of unc-7 mutants to that of the wild type level. (C) Heterologous expression of wild type UNC-7 in Neuro2A cells allowed electric coupling between cells, whereas cells expressing Cys-less UNC-7 did not induce coupling. (D) Localization of exogenously expressed UNC-7 in Neuro2A cells. Transfected Neuro2A cells were stained with anti-UNC-7 antibody (red) and GFP expressed from the same vector in the transfected cells (green). Wild type UNC-7 localized at junctions of two adjacent cells (white arrow), whereas Cys-less UNC-7 did not. Scale bar: 10 μm.