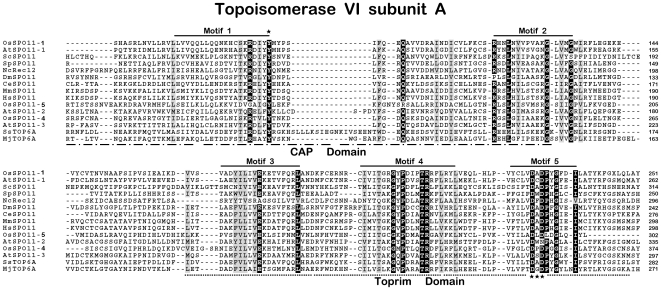
Figure 1. Multiple alignment of amino acid sequences of OsSpo11s and their homologues using ClustalX software (version 1.8).
Gaps are shown by dashes. Black boxes indicate conserved residues, and grey boxes indicate similar residues. The respective amino acid position of each sequence is given on the right. The active tyrosine residue and the DXD sequence identified in archaeal TopVIA are marked with asterisks in motif I and motif V, respectively. Sequences used here are OsSpo11-5C (accession No. AY154916), OsSpo11-1 (GU170363) and OsSpo11-4 (GU177866) from Oryza sativa; AtSpo11-1 (AJ251989), AtSpo11-2 (AJ251990) and AtSpo11-3 (AL162973) from Arabidopsis thaliana; ScSpo11 (P23179) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae; SpRec12 (P40384) from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; NcSpo11 (CAB88597) from Neurospora crassa; DmSpo11 (AAC61735) from Drosophila melanogaster; CeSpo11 (CAA92974) from Caenorhabditis elegans; MmSpo11 (Q9WTK8) from Mus musculus; HsSpo11 (Q9Y5K1) from Homo sapiens; SsTopVIA (O05208) from Sulfolobus shibatae and MjTopVIA (Q57815) from Methanobacterium janaschii.