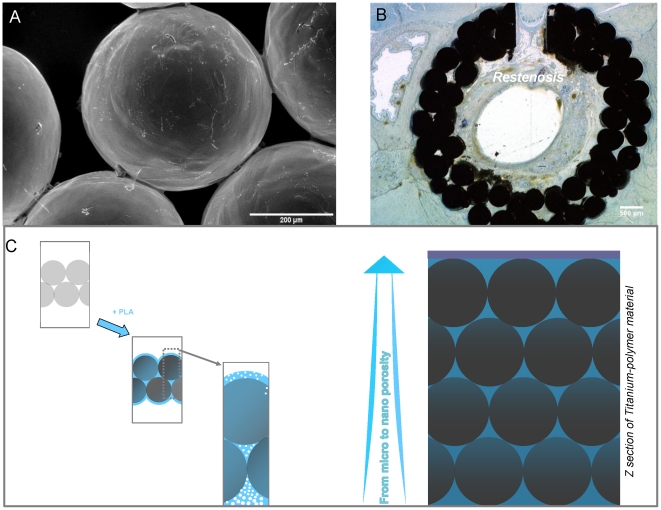
Figure 1. Occurrence of restenosis and proposed solution.
a) SEM observation displaying microscopic structure of macroporous titanium implants. b) When implanted(with a slice of native trachea left in place, as seen as a hole), tubular macroporous titanium implants are prone to development of restenosis in rats after 1 month of implantation and subsequent decrease in lumen diameter due to the fact that the open porous structure permits excessive movement of fibroblasts and inflammatory cells as observed by histological sections. c) The scheme of proposed hybrid material to control cell movement in both radial (fibroblasts) and longitidunal (epithelial cells) directions.